Introduction
Modern software development is no longer just about typing syntax; it is about orchestrating intelligence. As we move into 2025 and 2026, the sheer volume of code being generated by machines requires a structured approach. This is where AI coding frameworks step in. They provide the scaffolding that allows large language models (LLMs) to understand your specific codebase, follow your architectural patterns, and act as a force multiplier for your engineering team.
According to the JetBrains Developer Ecosystem Report 2025, the adoption of AI is no longer a “nice to have” but a core component of the professional workflow. More than two-thirds of professional developers now use some form of AI coding assistance, shifting the focus from “how do I write this function?” to “how do I design this system?”
Defining Modern AI Coding Frameworks and Assistants
When we talk about AI coding frameworks, we are referring to the integrated systems that facilitate the interaction between a developer, their code, and an AI model. These aren’t just simple chatbots; they are sophisticated environments capable of code generation, deep IDE integration, and complex context management.
The magic happens in how these tools handle “context.” A generic LLM knows how to write a Python script, but an AI coding framework knows how to write a Python script that uses your internal libraries, follows your naming conventions, and integrates with your specific database schema. This level of awareness is what separates a toy from a professional tool.
Tools like the JetBrains AI Assistant leverage this by living directly within the developer’s workflow. They don’t just suggest the next line of code; they assist with software architecture, refactoring legacy modules, and even generating documentation that actually makes sense. By automating the “boring” parts of coding, these frameworks allow us to focus on high-level logic and creative problem-solving.
Core Components of AI Coding Frameworks
To be considered a complete framework for AI-assisted development, a tool generally needs four pillars:
- Professional IDE Capabilities: A robust environment with debugging, version control, and syntax highlighting.
- AI Interaction Interface: A way to talk to the model, whether through a chat sidebar, inline ghost text, or terminal commands.
- Context Management: The ability to “read” the entire project folder, including READMEs and configuration files, to provide relevant answers.
- Advanced LLM Integration: The engine under the hood. Whether it’s GPT-4o, Claude 3.7, or a custom local model, Advanced LLM integration ensures the framework can reason through complex logic.
Evolution of Agentic Development
We are currently moving past simple “autocomplete” and into the era of “agentic” development. This involves task delegation and automated code verification. Instead of you writing the code and asking the AI to check it, you might tell an agent to “build a login page with OAuth support,” and it will generate the files, run the tests, and verify the quality itself.
A prime example of this evolution is Junie, a new AI coding agent focused on delegation. It can take a high-level task, break it down into steps, and execute them across multiple files. This shift toward autonomous agents means developers are becoming “code reviewers” for their AI counterparts, ensuring that the generated output meets the team’s standards.
Top Frameworks for Model Orchestration and Agents
Beyond the IDE, there is a whole world of AI coding frameworks designed to build the AI applications themselves. If you are building a custom AI tool for your business, you need orchestration. This involves managing RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) architectures, where the AI looks up information in your private documents before answering.
LangChain remains the titan in this space. It is a modular, open-source framework that allows us to chain different models and tools together. For example, you could build a workflow where an AI reads a customer support ticket, searches your documentation, writes a code fix, and then drafts a reply to the user.
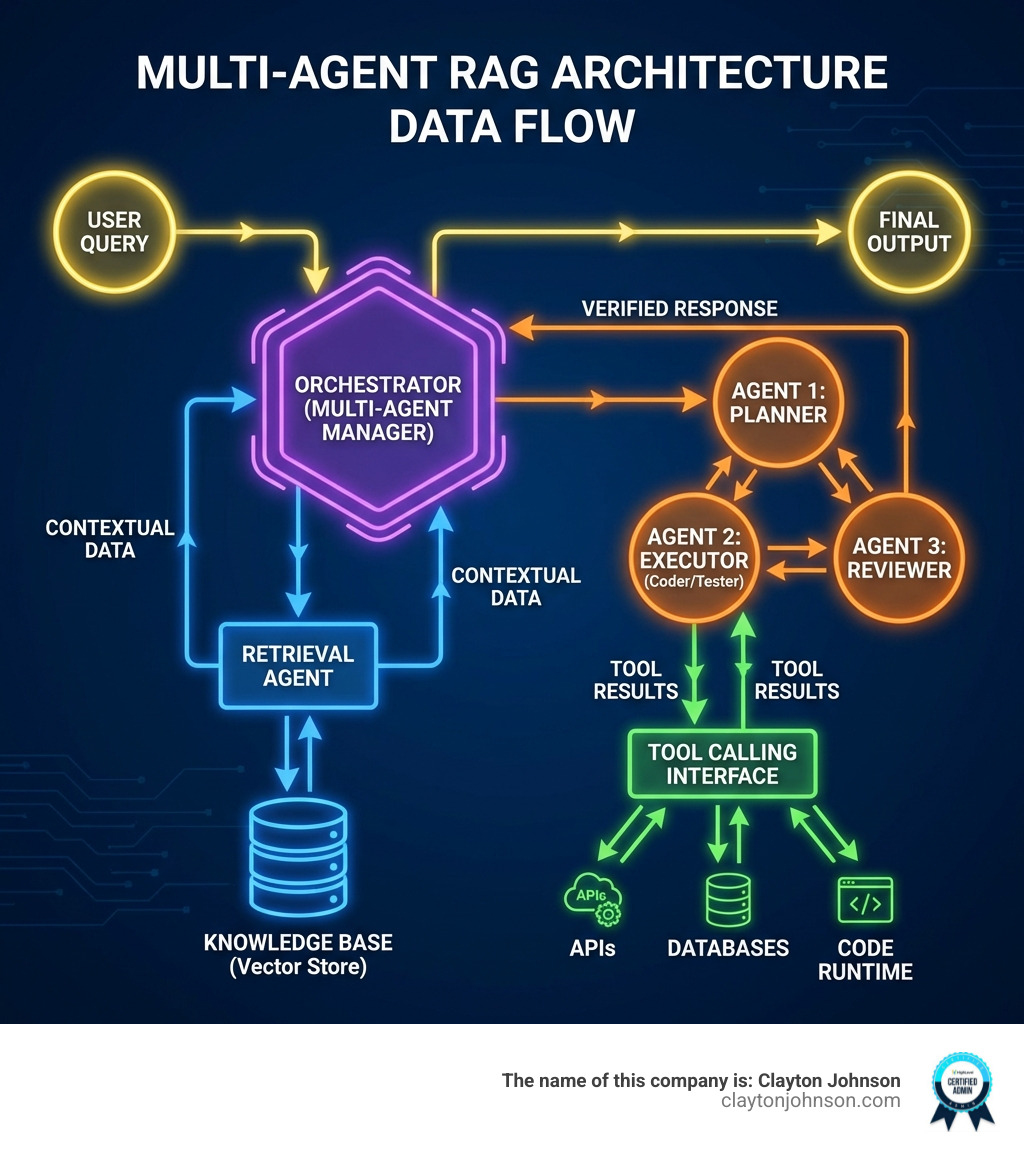
For those who prefer a more visual approach to workflow automation, n8n offers a powerful alternative. It combines the flexibility of traditional coding with a low-code interface, allowing you to connect over 400 different services. By using OpenAI Agents, you can build stateful workflows that remember previous interactions and handle complex tool-calling logic without writing hundreds of lines of boilerplate code.
Orchestrating Complex Workflows
As systems grow, a single AI agent often isn’t enough. We are seeing a trend toward “multi-agent systems” where different agents have specific roles. AutoGen by Microsoft is a leading framework for this, allowing agents to “talk” to each other to solve problems. One agent might be the “coder,” another the “reviewer,” and a third the “tester.”
Similarly, CrewAI focuses on role-based design. You can define a “crew” of agents, each with a specific persona and goal. This mimics a real-world software team and is incredibly effective for complex tasks like market research or full-stack feature development.
Visual and Low-Code Alternatives
Not every coding task requires a heavy-duty IDE. The State Of Low-Code, Global 2025 report highlights that low-code platforms remain a top investment for enterprises. These tools allow for rapid prototyping and, in many cases, offer higher production reliability than pure AI-generated code because they use battle-tested, pre-built components.
If you want to see this in action, you can Try n8n now. It’s particularly useful for DevOps and IT teams who need to build secure, scalable automations without the “hallucination” risks sometimes associated with pure LLM code generation.
Leading AI Coding Assistants and IDE Integrations
When it comes to daily coding, the “Big Three” environments are VS Code, JetBrains, and Xcode. Each has a different philosophy on how AI coding frameworks should behave.
| Feature | Cursor | GitHub Copilot | JetBrains AI Assistant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary IDE | VS Code (Fork) | Extension-based | Native to JetBrains |
| Best For | Power users / AI-first | General purpose | Professional/Enterprise |
| Model Choice | Claude 3.7 / GPT-4o | OpenAI / Anthropic | Multi-model switching |
| Context | Full Workspace | Repository-level | Deep IDE Integration |
Cursor has gained a cult following because it is a fork of VS Code built specifically for AI. It treats the AI as a first-class citizen rather than a plugin. On the other hand, GitHub Copilot remains the most widely used due to its massive ecosystem and seamless integration with GitHub repositories.
For Apple developers, Xcode’s AI features represent a significant step forward. Introduced in Xcode 16, these features use local models optimized for Apple silicon, ensuring that your code stays on your machine while still providing intelligent completions and chat interfaces.
Specialized AI Coding Frameworks for Web Apps
Sometimes you don’t want to set up a local environment at all. Browser-based IDEs like Bolt.new are changing the game for web development. Using WebContainers technology, Bolt.new allows you to build, run, and deploy full-stack applications entirely in your browser.
The Live app inspector in Bolt.new lets you see changes instantly, making it perfect for rapid deployment and prototyping. You can prompt the AI to “add a contact form,” and it will write the frontend, set up the backend API, and show you the working result in seconds.
CLI and Extension-Based Assistants
For those who live in the terminal, command-line interface (CLI) agents are the way to go. Aider is a popular choice that allows you to edit code in your local git repository using the terminal. It is famous for its “repository mapping” feature, which creates a condensed map of your entire project so the LLM understands the relationships between files without hitting token limits.
Another powerful extension is Cline, which brings agentic capabilities to VS Code. Unlike simple completion tools, Cline can proactively run terminal commands, read files, and edit code across your entire project based on your instructions.
Selection Criteria for Scalable AI Coding Frameworks
Choosing a framework isn’t just about which AI is “smartest.” For professional teams, security and compliance are the top priorities. The Ten Key Regulatory Challenges: 2025 Mid-Year report notes that regulatory pressure is forcing enterprises to emphasize RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) and audit logs.
When we evaluate AI coding frameworks for scale, we look at:
- Enterprise Readiness: Does it support SSO (Single Sign-On)? Does it have a SOC 2 report?
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the monthly subscription, what is the cost of the API tokens?
- Context Window: How much of your codebase can the model “see” at once?
- Integration: Does it play nice with your existing CI/CD pipeline?
Evaluating Open-Source AI Coding Frameworks
Open-source software (OSS) underpins 90% of enterprise production workloads. The 2025 State of Open Source Report shows that many teams are moving toward open-source AI models to maintain data sovereignty.
If you like the idea of Bolt.new but want to run it on your own servers, bolt.diy is a community-driven project that gives you full control. Self-hosting your AI coding frameworks ensures that your proprietary logic never leaves your firewall, which is a non-negotiable for many industries.
Proprietary vs. Local AI Coding Frameworks
The debate between cloud-based and local models usually comes down to a trade-off between accuracy and privacy.
- Proprietary (Cloud): Models like Claude 3.7 and GPT-4o are incredibly powerful and fast. They are the “gold standard” for complex reasoning.
- Local LLMs: Using tools like Ollama or llama.cpp, you can run models like DeepSeek or Llama 3 on your own hardware. While they might be slightly less “smart” than the top-tier cloud models, they offer 100% privacy and zero latency from internet issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best AI coding framework for beginners?
For those just starting, we recommend low-code platforms or frameworks with high-level APIs. Keras and Scikit-Learn are fantastic for learning the basics of machine learning because they have clean, simple syntax. If you want to build applications without getting bogged down in complex code, you should sign up for a free n8n cloud account. It allows you to experiment with AI logic visually, which is a great way to build mental models of how these systems work.
How do AI coding tools handle data privacy?
Data privacy varies by tool. Most enterprise-grade frameworks offer “zero-retention” policies, meaning they don’t use your code to train their future models. For maximum security, look for tools that support local execution or provide enterprise encryption. As mentioned in the Ten Key Regulatory Challenges: 2025 Mid-Year report, audit logs and environment separation are key features to look for if you are in a regulated industry.
Can I use multiple AI models within one framework?
Yes! In fact, we encourage it. Many modern tools, like the JetBrains AI Assistant, allow you to switch between models. You might use GPT-4o for quick code completions but switch to Claude 3.7 for a complex architectural review. This API flexibility ensures you always have the best “brain” for the specific task at hand.
Conclusion
Selecting the right AI coding frameworks is about more than just following trends; it’s about building a scalable foundation for your development team. Whether you are using a native IDE assistant like JetBrains, orchestrating multi-agent crews with LangChain, or building secure automations with n8n, the goal is the same: to move faster without breaking things.
At Clayton Johnson, we focus on growth strategy and technical systems that deliver measurable results. When AI is rapidly changing the rules of the game, future-proofing your development workflow is the best investment you can make. If you’re looking to scale your presence in the Twin Cities or beyond, our SEO services Minneapolis can help you steer this new landscape with AI-assisted workflows that actually work.

Ready to optimize your tech stack? Start by evaluating your current bottlenecks and testing one of the frameworks we’ve discussed today. The future of coding is collaborative—make sure your AI partner is the right fit for the job.