The Art of Turning the Web into AI Datasets
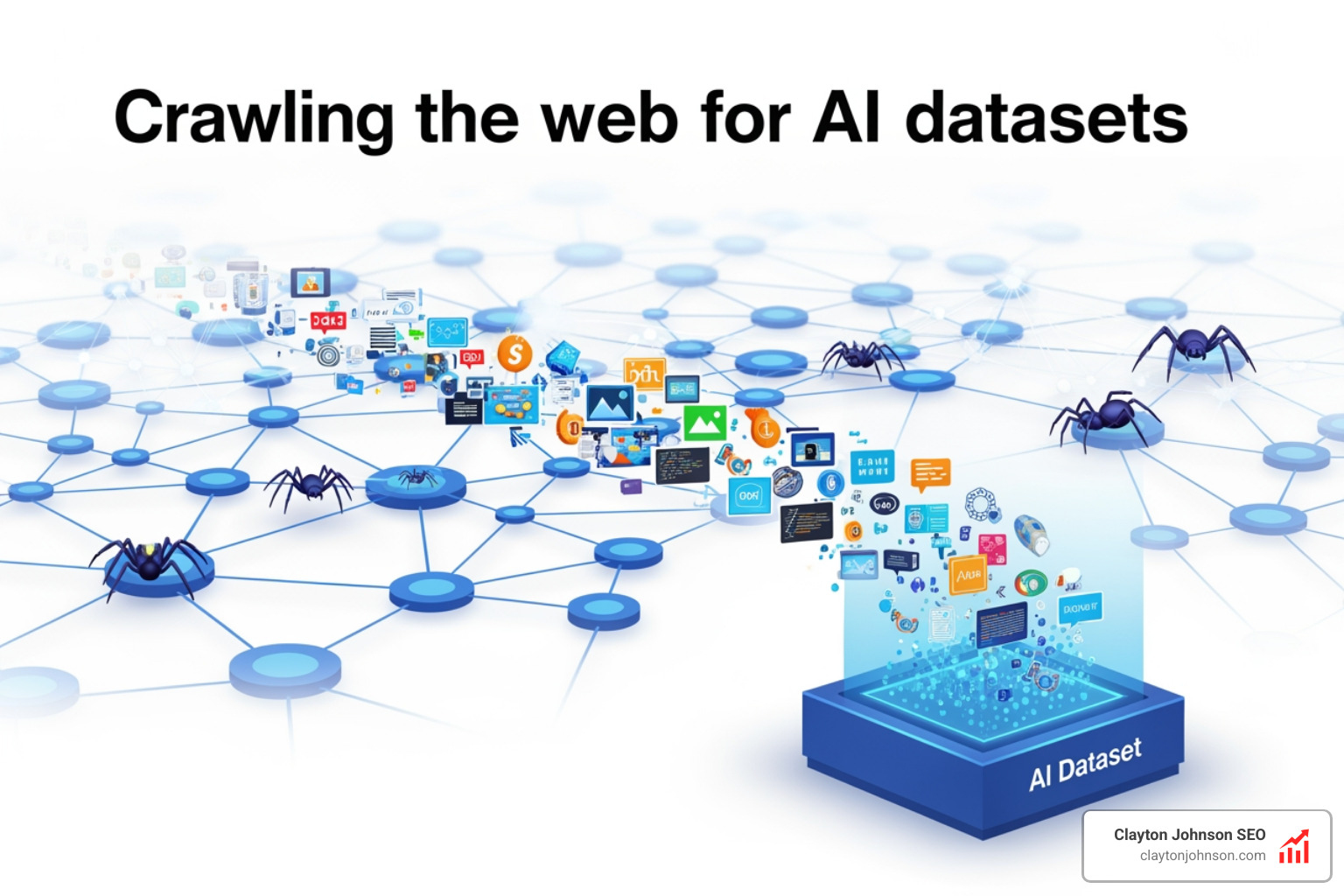
Crawl web for ai datasets is the foundational step that determines whether your AI model will be brilliant or mediocre. Every major language model—from GPT to Claude to Llama—depends on massive amounts of clean, structured web data. But here’s the problem: over 90% of raw web crawl data gets thrown away during LLM pretraining because it’s low quality, redundant, or irrelevant.
Quick Answer: How to Crawl Web for AI Datasets
- Choose your tool – Use Firecrawl for clean markdown, Common Crawl for massive free datasets, or Exa for high-quality filtered data
- Handle dynamic content – Deploy headless browsers and rotating proxies to bypass anti-bot measures
- Filter for quality – Apply pretraining influence scores to prioritize valuable pages over random content
- Structure for training – Convert HTML to markdown, remove navigation fluff, and chunk by token limits
- Respect boundaries – Follow robots.txt, respect copyright, and avoid overloading servers
The shift from random web crawling to quality-first data collection is transforming how AI teams build datasets. Traditional crawlers like PageRank-based systems collect billions of pages but discard most of them. New research shows that tools like Craw4LLM can achieve the same model performance while crawling only 21% of the URLs by prioritizing pages with high pretraining value.
Common Crawl maintains over 300 billion pages spanning 15 years and adds 3-5 billion new pages monthly—all free and open. Commercial tools like Firecrawl convert messy websites into LLM-ready markdown without requiring sitemaps. Exa curates custom datasets up to trillions of tokens using natural language filters. Each approach solves different problems in the data pipeline.
The technical challenges are real: JavaScript rendering, anti-bot protections, CAPTCHA walls, rate limiting, and distinguishing useful content from boilerplate. Modern tools address these with headless browsers, residential proxies, and intelligent HTML cleaning that removes navigation, ads, and other “fluff.”
But efficiency isn’t just about tools—it’s about crawling strategy. Research from Carnegie Mellon demonstrates that prioritizing URLs based on pretraining influence scores (rather than link popularity) reduces data waste by 79% while maintaining 95% of model performance. This means faster collection, lower costs, and less burden on web infrastructure.
I’m Clayton Johnson, and I’ve built SEO and growth systems that depend on structured data extraction from the web—including crawl web for ai datasets workflows that power content intelligence and competitive analysis. This guide walks through the tools, techniques, and ethical frameworks you need to build high-quality AI training datasets from web sources.

Why You Must Crawl Web for AI Datasets Today
In the current AI arms race, data is the new oil. However, unlike oil, the internet is full of “sludge”—low-quality content, ads, and duplicate pages. If we simply vacuum up the entire internet without a plan, we end up with a massive storage bill and a model that hallucinates or provides poor information.
Statistics show that over 90% of raw data collected from massive web crawls is discarded during LLM pretraining because it fails quality checks. This waste is a massive drain on computational resources. To build better models, we need to transition from “wholesale collection” to “intelligent discovery.” By focusing on pretraining influence—the likelihood that a piece of data will actually help a model learn—we can build smarter datasets with less overhead.

Understanding the nuances of how websites refuse crawlers is also vital. Scientific research on web crawl refusals highlights that inconsistent and poorly signaled blocking can lead to incomplete datasets. For developers in Minneapolis and beyond, mastering these hurdles is the difference between a robust dataset and a broken pipeline. If you’re looking to enhance your overall digital strategy while building these tools, you can Boost Your Rankings with These Free SEO AI Tools to ensure your own sites are optimized for the AI-driven search era.
Overcoming Challenges to Crawl Web for AI Datasets
The modern web is a fortress. Gone are the days of simple HTML pages that you could scrape with a basic script. Today, we face:
- Anti-bot Measures: Advanced firewalls and CAPTCHAs designed to keep automated scripts out.
- Dynamic Content: Websites built with React, Vue, or Angular that don’t reveal their content until a browser executes their JavaScript.
- IP Blocking: Servers that quickly ban any IP address making too many requests in a short window.
To crawl web for ai datasets effectively, we must use headless browsers (like Playwright or Puppeteer) that simulate a real human user. We also rely on rotating residential proxies to mask our origin and avoid rate limits. These technical hurdles are exactly why we recommend performing AI-Driven SEO Audits to understand how modern search engines—and AI crawlers—perceive your site’s technical health.
The Role of Common Crawl in Open Research
If you want to go big without a massive budget, you start with Common Crawl. This 501(c)(3) non-profit has been the backbone of AI research since 2007.
- Scale: Over 300 billion pages spanning 15 years.
- Freshness: 3–5 billion new pages added every single month.
- Accessibility: A free and open Common Crawl repository that anyone can analyze.
Common Crawl has been cited in over 10,000 research papers and was a primary data source for the original GPT models. It allows for wholesale extraction and transformation of the open web, making it an indispensable resource for researchers. However, because it is a general crawl, it requires heavy filtering to find high-quality content. Using this data effectively can even help you understand the broader landscape of Google Rankings by analyzing how millions of sites link to one another.
Top Tools for Scraping and Structuring AI Data
Building a dataset from scratch is hard, which is why a new ecosystem of “AI-first” crawlers has emerged. These tools don’t just give you HTML; they give you clean, structured data that an LLM can actually understand.
Comparison of Top Web Crawling Tools
| Feature | Firecrawl | Common Crawl | Exa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Clean markdown for RAG/Apps | Massive pretraining datasets | Semantic search & curated sets |
| Cost | Commercial API (Free tier) | Free (Open Source) | Commercial API |
| JS Rendering | Built-in | Limited | Built-in |
| Filtering | CSS/Schema based | Needs manual post-processing | Natural language filters |
| Scale | Site-specific / Batch | Entire Web | Trillions of tokens |
Firecrawl: Converting URLs to LLM-Ready Markdown
Firecrawl is currently the “gold standard” for developers who need to turn a URL into clean data. Unlike traditional crawlers that require you to build a sitemap or define complex regex patterns, Firecrawl crawls all accessible subpages automatically.
The Firecrawl API documentation reveals its true power: it handles proxies, anti-bot mechanisms, and media parsing (like PDFs and images) right out of the box. For Python developers, the Python SDK for Firecrawl makes it easy to integrate crawling into your existing AI workflows with just a few lines of code.
from firecrawl import FirecrawlApp
app = FirecrawlApp(api_key="YOUR_API_KEY")
crawl_result = app.crawl_url('https://claytonjohnson.com', params={'limit': 100})
By stripping away the “fluff”—navigation bars, ads, and footers—Firecrawl ensures your tokens are spent on actual content. This is a crucial step when using The Top Automated SEO Audit Tools for Faster Rankings, as clean data is much easier for AI to audit and optimize.
Exa and Apify: High-Quality Filtering and RAG Integration
While Firecrawl is great for deep-diving into specific sites, Exa is built for semantic discovery. Exa allows you to use natural language queries to find data. Instead of searching for “financial news,” you can ask for “articles mentioning S&P 500 companies in the last year,” and Exa will provide a custom dataset. This Exa dataset curation can scale to trillions of tokens, providing a high-quality alternative to the “randomness” of Common Crawl.
Apify offers a different strength: the “Website Content Crawler.” This tool is specifically designed to feed vector databases. Through the Apify LangChain integration, you can crawl a documentation site and immediately push that data into a RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) system. This is perfect for building custom chatbots that actually know your product. For those managing large-scale content, these are the Top AI Content Audit Tools for Smarter Websites that save hundreds of hours of manual review.
Advanced Strategies for Efficient Data Collection
The most significant advancement in this field is moving away from graph connectivity (like PageRank) and toward pretraining influence.
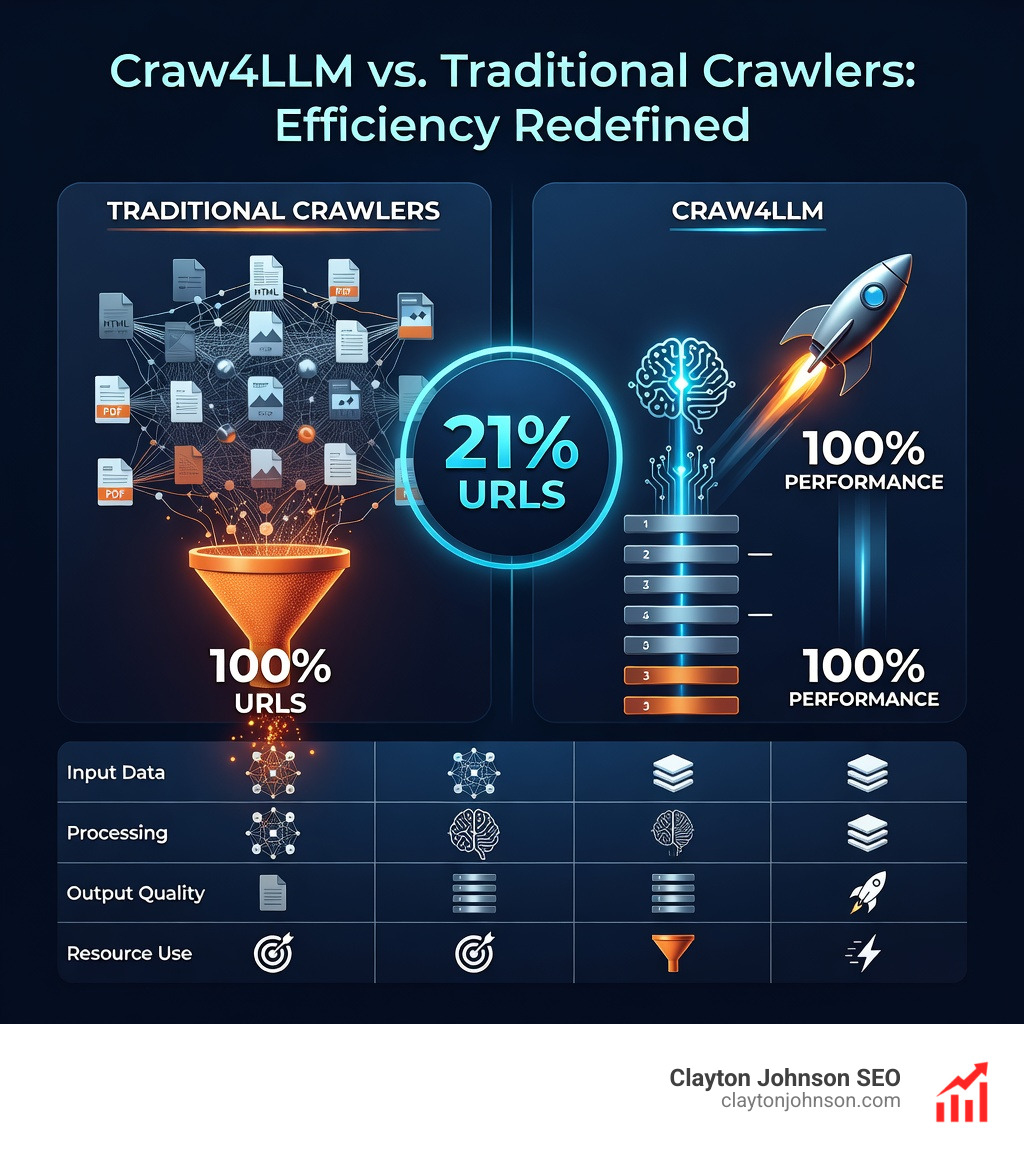
Traditional crawlers prioritize pages that have the most links pointing to them. But in AI, a popular page isn’t necessarily a high-quality page. A viral tweet might have millions of links, but a deeply researched scientific paper might only have a few.
Using Craw4LLM to Crawl Web for AI Datasets
The Research on Craw4LLM efficiency has changed the game. Craw4LLM uses LLM-based scorers (like DCLM fastText) to evaluate a page’s quality during the crawl. If a page is high quality, the crawler prioritizes its outgoing links.
The results are staggering:
- 21% Efficiency: Craw4LLM achieves the same LLM performance as traditional crawlers while only visiting 21% of the URLs.
- Oracle Performance: It can reach 95% of “oracle performance” (the best possible data) while crawling only 2.2% of the total available web graph.
By focusing on quality early, we reduce the burden on web servers and save massive amounts of storage and compute. You can check out the Craw4LLM GitHub repository to see how to implement these priority scores in your own projects. This approach aligns perfectly with our philosophy of Content Auditing for Humans Who Use Robots—using AI to do the heavy lifting of quality control.
Integrating with LLM Frameworks like LangChain and Crew.ai
Once you’ve crawled the data, you need to put it to work. Most modern developers use frameworks like LangChain or LlamaIndex to connect their datasets to models.
The LangChain Firecrawl loader allows you to load crawled pages directly as “Documents” in your code. From there, you can:
- Split the text into chunks (usually around 500 tokens).
- Generate embeddings using models like
text-embedding-ada-002. - Store in a Vector Database like Pinecone or Qdrant.
This enables “automated agents” (using tools like Crew.ai) to research the web in real-time, find answers, and summarize findings without human intervention. This is a core part of the SEO Services we offer, where we use AI-assisted workflows to diagnose growth problems and execute content strategies at scale.
Ethical Crawling and Compliance for LLM Training
We can’t talk about crawl web for ai datasets without talking about ethics. Just because data is public doesn’t mean it’s a free-for-all.
- Robots.txt: Always check this file. It’s the “No Trespassing” sign of the internet.
- GPTBot vs. OAI-SearchBot: OpenAI now allows you to distinguish between their bots. You can allow
OAI-SearchBotso your site appears in ChatGPT search results, while blockingGPTBotif you don’t want your data used to train their foundational models. - Rate Limiting: Don’t be a jerk. If you hit a small website with 1,000 requests per second, you’ll crash their server. Use “polite” crawling settings.
For more details on managing these controls, refer to the official OpenAI crawler controls. Staying compliant isn’t just about being a good digital citizen; it’s about protecting your project from legal risks. If you want to see how your own site measures up against these bots, check out The Best Ways to Get a Free AI SEO Audit Today.
Frequently Asked Questions about AI Data Crawling
How large is the Common Crawl dataset?
Common Crawl is massive. It contains over 300 billion pages collected over 15 years. Every month, the team adds another 3 to 5 billion pages to the archive. It’s currently petabytes in size and is the most cited dataset in AI research.
What is the difference between GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot?
GPTBot is OpenAI’s crawler used specifically to gather data for training their generative AI models. OAI-SearchBot is used to index websites so they can appear as citations and search results within ChatGPT’s real-time search feature. You can block one while allowing the other in your robots.txt file.
Is web scraping legal for AI training?
Generally, web scraping for public, non-personal data is legal in the United States (following the HiQ vs. LinkedIn precedent). However, you must respect the website’s Terms of Service and robots.txt. Additionally, while scraping might be legal, republishing copyrighted content or using it in a way that violates “Fair Use” can lead to legal challenges. Always consult with legal counsel for large-scale commercial projects.
Conclusion
Turning the web into an AI dataset is a sophisticated art form. It requires a balance of technical muscle—handling JavaScript and anti-bot walls—and strategic finesse—prioritizing high-quality data to reduce waste. Whether you are using the massive reach of Common Crawl, the clean markdown of Firecrawl, or the efficient quality-scoring of Craw4LLM, the goal remains the same: build a dataset that makes your AI smarter.
At Clayton Johnson SEO, we specialize in these AI-assisted workflows. Based in Minneapolis, Minnesota, we help founders and marketing leaders navigate the complex world of SEO strategy and data growth. If you’re ready to turn your web presence into a measurable growth engine, explore our Minneapolis SEO services and let’s build something brilliant together.