How AI Assisted Code Migration Saves Months of Work
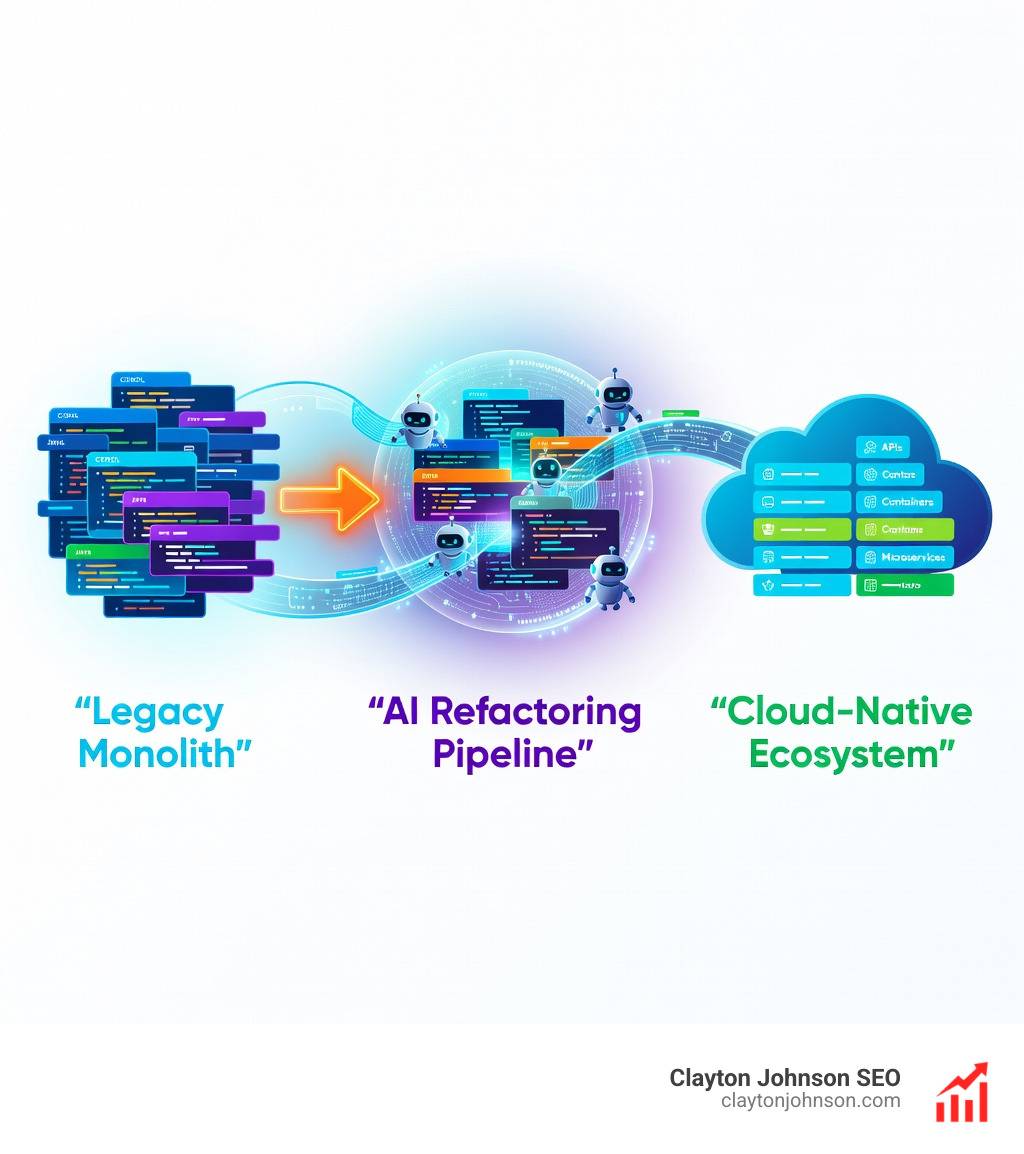
Why Legacy Code Migration Is Finally Solvable at Scale
AI assisted code migration is transforming how enterprises modernize legacy systems by automating repetitive code transformations, dependency analysis, and validation—reducing project timelines by up to 60% while maintaining business logic integrity.
Key Benefits of AI Assisted Code Migration:
- Speed: Migrations that would take 2 years manually now complete in 4 months
- Accuracy: 93% structural completeness for simple files, 81% for medium complexity
- Scale: Handle 14,000+ files without expanding engineering headcount
- Cost: Reduce manual effort by 50% while doubling code surface area
- Quality: Automated validation loops catch regressions before production
If you’ve ever stared at a COBOL system from 1997 or a tightly-coupled Java monolith and wondered how to modernize it without breaking everything, you’re not alone. Legacy code migration has historically been the job nobody wants—time-consuming, risky, and boring. According to the 2024 DORA Report, 67% of developers now report that AI is helping them improve their code, yet most still spend more time modifying existing code than writing new code.
The problem isn’t just technical. It’s architectural, organizational, and often undocumented. Where do you draw service boundaries when the original architects are long gone? How do you handle data consistency across distributed services when your database thinks foreign keys are optional? What gets migrated first when three different VPs claim everything is “mission-critical”?
AI doesn’t solve these strategic puzzles—but it does handle the grunt work that makes them solvable. It excels at code archaeology (tracing dependencies across thousands of files), pattern recognition (spotting inconsistent logic implementations), and mechanical transformations (converting deprecated APIs at scale). The result is a hybrid workflow where AI tackles repetitive tasks while human architects focus on business logic, risk assessment, and strategic decisions.
As Clayton Johnson, I’ve spent years building SEO and growth systems that rely on structured workflows and measurable outcomes—principles that apply directly to AI assisted code migration, where clear frameworks, validation loops, and iterative refinement turn chaotic legacy systems into maintainable modern architectures.

Learn more about ai assisted code migration:
The Core Challenges of Legacy Code Migration
Legacy code migration is often compared to cleaning a house that hasn’t been touched in decades. It is a necessary evil, yet it is often viewed as a cost center because it doesn’t always add immediate business value. For many organizations, the sheer volume of code is the first hurdle. We see systems with millions of lines of code, where “Bob from Accounting” wrote a quick fix in 1997 that is now the backbone of a multi-billion dollar transaction engine.
The technical challenges are immense:
- Undocumented Patterns: Legacy systems are full of “magic” logic that no one remembers.
- Architectural Puzzles: Moving from a monolith to microservices isn’t just a syntax change; it’s a fundamental shift in how data flows.
- Deep Dependencies: Changing one API call can have a ripple effect across thousands of files.
- Data Integrity: Ensuring that your new Java service treats data exactly like the old COBOL program is incredibly difficult.

Without ai assisted code migration, these projects often stall. Research shows that manual migrations are prone to human error and high regression risks. For example, a project that was estimated to take two years of manual labor can often be condensed into just four months by leveraging AI.
| Feature | Manual Migration | AI-Assisted Migration |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | 1.0x (Baseline) | 2.5x – 3x faster |
| Error Rate | High (Human fatigue) | Low (Pattern-based consistency) |
| Documentation | Often skipped | Automatically generated |
| Scalability | Limited by headcount | Virtually unlimited |
| Cost | High (Engineering hours) | Lower (Tooling + targeted review) |
To effectively tackle these hurdles, we must look at how to master AI coding workflows on GitHub to bring structure to the chaos. Organizations that fail to modernize risk data compatibility issues and operational bottlenecks that can bring business to a halt. As noted in Sourcegraph’s migration documentation, the risk of doing nothing often outweighs the cost of the migration itself.
Architecting an AI Assisted Code Migration Workflow
To move beyond simple “chat-based” coding and into enterprise-grade transformation, we need a structured, agentic architecture. This isn’t about asking an LLM to “rewrite this app.” It’s about building a factory where specialized AI agents handle specific parts of the code migration process.
We typically see success using a multi-agent orchestration framework. For instance, using the Amazon Bedrock Converse API with models like Amazon Nova Premier allows for a systematic approach. This “agentic” workflow ensures that the migration isn’t a single “black box” event but a series of verifiable steps.
Google has pioneered this by using AI to author 80% of code modifications in large-scale projects, such as migrating 32-bit IDs to 64-bit integers. Their research on accelerating code migrations with AI highlights that a single engineer can manage massive changes that previously required entire teams. By adopting a multi-model strategy—using different models for analysis, transformation, and testing—we can maximize the strengths of each.
To understand how this fits into your existing setup, check out the complete guide to how Claude helps your coding workflow.
Handling Token Limitations in AI Assisted Code Migration
One of the biggest “gotchas” in large-scale migration is the context window. If you try to feed a 2,000-line legacy file into a model with a small token limit, the AI will lose the plot halfway through. We handle this through a technique called text prefilling and response stitching.
By using the Bedrock Converse API, we can monitor the stopReason. If a model stops because it hit the max_tokens limit, the system can automatically continue the generation by prefilling the next prompt with the last few lines of the previous output. This maintains context across massive files. We also use “RAG” (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) to give the AI access to the broader codebase without overwhelming the immediate prompt.
You can learn more about building these capabilities in our guide on how to extend Claude with custom agent skills.
The Role of Specialized Agents in AI Assisted Code Migration
In a high-performing ai assisted code migration pipeline, we don’t use one general-purpose bot. We use specialized agents:
- Analysis Agent: Scans the legacy codebase to identify technical debt, deprecated APIs, and complex logic blocks.
- Conversion Agent: Performs the actual translation (e.g., C to Java or Apex to Spring Boot) based on predefined transformation rules.
- Security Agent: Scans the new code for vulnerabilities that might have been introduced during translation.
- Validation Agent: Automatically generates unit tests and runs them to ensure functional parity with the old system.
This “critique-loop” architecture, often discussed in Computer Science and Software Engineering research, allows the AI to self-correct. If a validation test fails, the Refine Agent takes the error log and the code back to the Conversion Agent for a second pass.
Dependency Analysis and Leaf-to-Root Sequencing
You can’t just migrate files in alphabetical order. If File A depends on File B, you should probably migrate File B first. We use dependency-graph-driven leaf-to-root sequencing.
By identifying “leaf nodes”—files with the fewest dependencies—the AI can build a stable foundation of modernized code. As the migration moves up the “root,” the AI has a library of already-migrated modern references to call upon. This was a key strategy in the Salesforce Core migration, where thousands of Apex files were refactored into Java. Starting at the leaves prevents the “hallucination” of missing references and ensures that scalable coding frameworks are implemented consistently.
Best Practices for Enterprise-Grade AI Assisted Code Migration
To ensure your migration doesn’t become a “Franken-system,” we recommend these proven best practices:
- Human-in-the-Loop: AI should be treated as a “smart junior engineer.” A senior architect must review strategic decisions, such as service boundaries and security protocols.
- Validation Loops: Never accept AI code that hasn’t passed a unit test. High-performing teams integrate automated testing into every step of the migration.
- Security Guardrails: Use tools like Sourcegraph’s Guardrails to prevent the AI from replicating copyrighted code or introducing known CVEs.
- Start Small: Run a “pilot flow.” Modernize one bounded module (like a report generator or a specific API) before attempting an enterprise-wide shift.
- Standardize Naming: AI can be inconsistent with variable names. Use an “Integration Agent” to enforce naming conventions across the new codebase.
For a deeper dive into the tools that make this possible, see our review of AI code review tools. Many of these strategies are also detailed in The Code Modernization Playbook, which emphasizes systematic transformation over “magic” one-click solutions.
Common Questions on Modernizing Legacy Systems
How does AI handle different migration types like language upgrades?
AI assisted code migration is versatile. For language upgrades (like Python 2 to 3), it excels at identifying syntax changes. For framework changes (like moving from Monolith to Microservices), it acts as an architectural assistant, helping to map out new service boundaries. Even complex architectural refactoring becomes easier when AI handles the “mechanical” work of moving logic into new service layers. This is why every developer needs AI tools in 2025.
What role does human oversight play in strategic decisions?
While AI can rewrite 10,000 lines of code in minutes, it doesn’t understand your company’s risk tolerance or customer SLAs. Humans are essential for:
- Strategic Review: Deciding what to migrate and when.
- Business Logic Validation: Ensuring the “weird edge case” from 1997 is still handled correctly.
- Architectural Design: Drawing the lines between new microservices.
AI handles the “how,” but humans still decide the “why.”
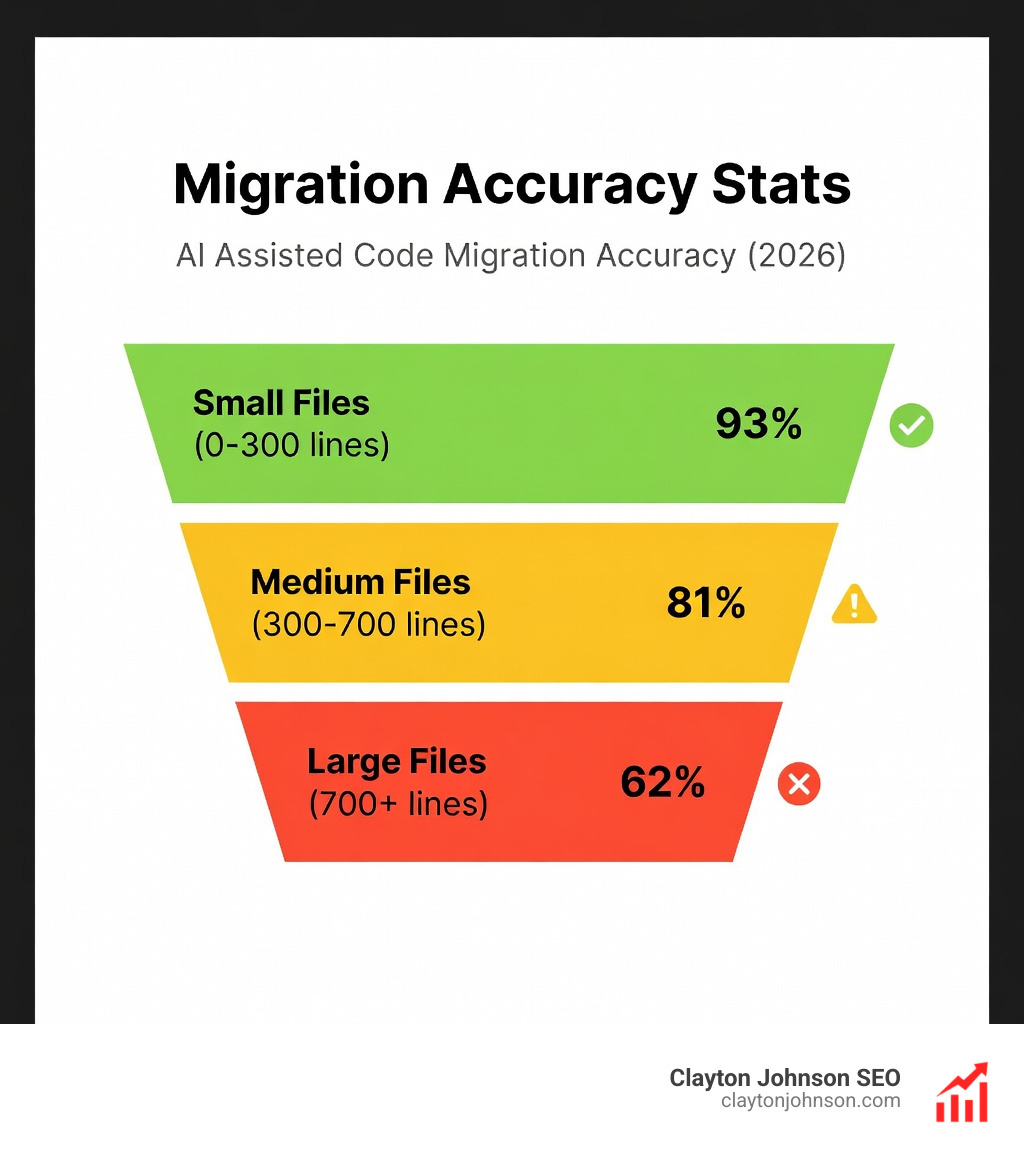
What are the proven accuracy rates for large-scale migrations?
The numbers are impressive but vary by file size:
- Small Files (0-300 lines): 93% structural completeness and 100% framework compliance.
- Medium Files (300-700 lines): 81% completeness (usually requiring 3-5 feedback cycles).
- Large Files (700+ lines): 62% completeness, often requiring manual refinement for complex business logic.
Overall, AI delivers a 2-3x productivity boost. In Google’s monorepo, over 75% of AI-generated character changes successfully “landed” in production.
Conclusion
The era of the “two-year manual migration” is coming to an end. By leveraging ai assisted code migration, organizations in Minneapolis and beyond can finally address their mounting technical debt without halting new feature development. The key is to move away from the “fantasy” of a magic button and toward the reality of a structured, agentic workflow.
At Clayton Johnson SEO, we believe in the power of AI-assisted workflows to drive growth and efficiency. Whether you’re optimizing a content system or modernizing a legacy codebase, the principles of measurement, iteration, and strategic human oversight remain the same.
Ready to scale your technical infrastructure?