Why Mastering Claude Prompts Transforms Your Development Workflow
Best Claude coding prompts are the difference between getting generic code suggestions and production-ready solutions that actually work. Here’s what separates effective Claude prompts from amateur attempts:
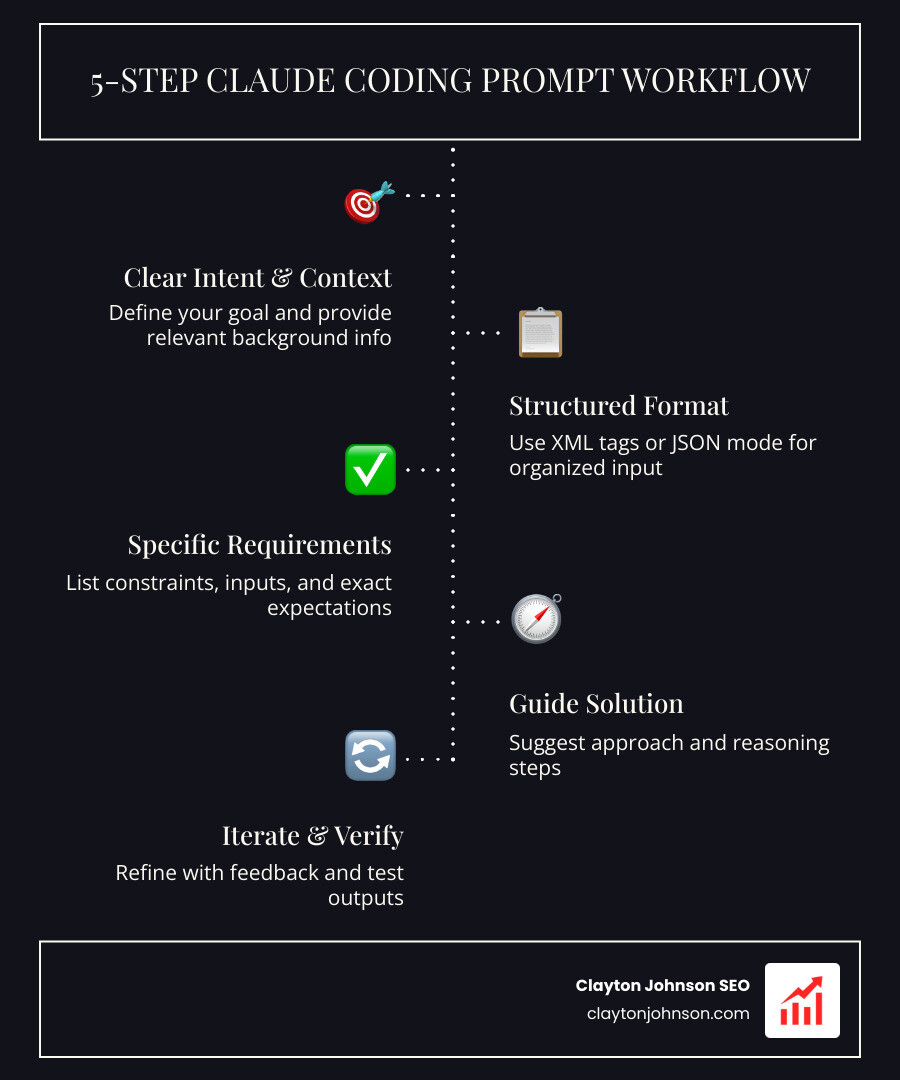
Essential Elements of Effective Claude Coding Prompts:
- Clear intent – State exactly what you’re building and why
- Explicit requirements – Define language, framework, edge cases, and error handling
- Specific context – Include relevant code, architecture details, and constraints
- Structured output – Use XML tags or JSON mode to control response format
- Guided approach – Tell Claude how to solve the problem, not just what the problem is
Quick Examples:
- ❌ “Make this code better”
- ✅ “Refactor this Python function to use async/await, add type hints, and handle network timeouts gracefully”
The research shows a clear pattern: developers who treat Claude like a “very fast intern with perfect memory” get dramatically better results than those who fire off vague one-liners. Anthropic’s own data reveals that XML-structured prompts produce up to 39% better outputs compared to unstructured requests.
The key insight? Claude can’t read your mind. It needs you to explicitly describe your technical stack, paste relevant code, specify conventions, and guide it toward the solution approach. When you provide rich context through tools like CLAUDE.md files and structure your requests with clear requirements, Claude shifts from a code completion tool to an intelligent development partner.
I’m Clayton Johnson, and through years of building SEO systems and AI-augmented workflows, I’ve refined best Claude coding prompts that consistently generate clean, maintainable code. This guide distills battle-tested patterns from production environments into copy-paste templates you can use immediately.
Best Claude coding prompts terms explained:
The Anatomy of the Best Claude Coding Prompts
To get the most out of Claude, we need to understand that prompt engineering isn’t just about asking nicely; it’s about providing a structured environment where the AI can succeed. The best Claude coding prompts follow a predictable anatomy.
Clarity, Explicitness, and Specificity
Vagueness is the enemy of good code. When we prompt Claude, we must be clear about our intent, explicit about the constraints, and specific about the context. For instance, if you’re working on a mastering-the-claude-ai-code-generator-for-faster-development workflow, you shouldn’t just say “fix the bug.” You should say, “The user is seeing a 404 error when clicking the ‘Submit’ button on the registration form; check the API route mapping in routes/auth.js.”
Using Structured Frameworks: XML and JSON
One of Claude’s unique strengths is its affinity for XML tags. Anthropic recommends wrapping different parts of your prompt in tags like
Furthermore, if you need data you can pipe directly into another tool, use JSON mode. By prefilling the response with an open curly bracket {, you essentially force Claude to respond in a structured data format. You can learn more about these nuances through Anthropic’s Prompt Engineering Interactive Tutorial.

Pro Strategies: From Planning to Execution
Amateurs jump straight into “Write me a function that…” Pros start with a plan. This is the “Plan Before You Code” discipline. Before a single line of code is written, we ask Claude to analyze the requirements and propose a technical approach.
The “Plan Before You Code” Discipline
When we use Claude for complex tasks, we often use a two-step process:
- The Architect Phase: “Analyze these requirements and create a technical specification in
SPEC.md. Identify potential edge cases and architectural risks.” - The Implementation Phase: “Based on the approved
SPEC.md, implement the data layer.”
This approach, detailed in our guide on the-best-ai-for-coding-and-debugging, ensures that the AI doesn’t start hallucinating a solution to a problem it doesn’t fully understand.
Leveraging Agentic Tools
If you are using the Claude Code CLI, you aren’t just limited to chat. You have access to a suite of agentic tools like BashTool, GrepTool, and GlobTool. These allow Claude to actually see your file system, search for patterns, and run tests.
| Feature | Standard Chat Prompt | Agentic Claude Code Command |
|---|---|---|
| Context | You must paste the code manually | Claude reads the files directly from your disk |
| Verification | You hope the code works | Claude runs npm test and fixes failures |
| Search | You find the file for Claude | Claude uses grep to find the relevant logic |
| Iteration | You copy-paste errors back | Claude monitors the terminal output and iterates |

Mastering Best Claude Coding Prompts for Debugging
Debugging is where Claude truly shines, but only if you provide the right “scent.” Don’t just describe the symptom; guide the solution.
A famous example from the FSCrawler documentation involves fixing a sluggish UI. A bad prompt says, “The UI is slow, fix it.” A best Claude coding prompt says: “The UI is sluggish during search results rendering. It feels like something is blocking the main thread. Look for non-async operations in the search controller and refactor them to be asynchronous.”
When debugging, always include:
- The full error traceback.
- The relevant environment details (Node version, OS, etc.).
- The code context (20-50 lines around the error).
- Any recent changes that might have triggered the bug.
Best Claude Coding Prompts for Full-Stack Development
For full-stack developers, Claude is a Swiss Army knife. Whether you are building React components or PostgreSQL schemas, the goal is to provide a “template” for success. Check out the-complete-claude-skill-pack-for-modern-developers for a deep dive into these workflows.
The API Endpoint Prompt Template:
“Create a POST endpoint for user registration using FastAPI.
- Use Pydantic for input validation.
- Hash passwords using Argon2.
- Return a JWT on successful registration.
- Include unit tests using Pytest.
“
We are using a PostgreSQL database with SQLAlchemy.
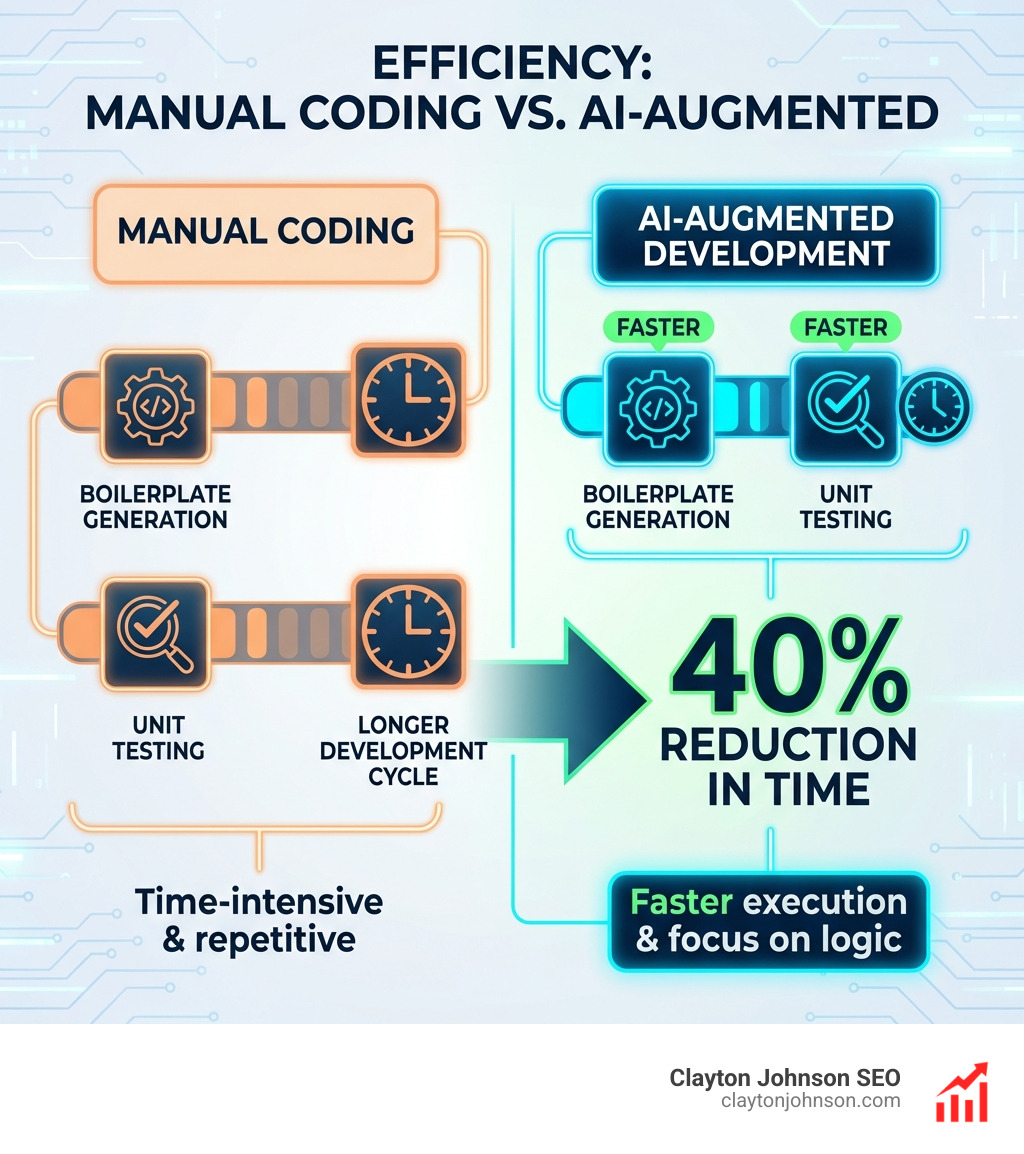
Advanced Techniques for Precision Output
Once you’ve mastered the basics, it’s time to look at how to make Claude a permanent part of your engineering “brain.”
Model Context Protocol (MCP) and CLAUDE.md
One of the most powerful recent additions is the Model Context Protocol (MCP). This allows Claude to connect to external tools like Jira, Google Drive, or your own custom API documentation.
Furthermore, we recommend maintaining a CLAUDE.md file in the root of your project. This file acts as a persistent memory bank. It should contain:
- Build and test commands.
- Code style preferences (e.g., “We prefer functional components over classes”).
- Architecture overviews.
- Project-specific “gotchas.”
Claude reads this file at the start of every session, ensuring it stays grounded in your specific repo’s standards. This is a core part of why-every-developer-needs-ai-tools-for-programming-in-2025.
Automating with Slash Commands and GitHub Actions
You can standardize your team’s workflow by creating custom slash commands. For example, a /review command can be programmed to run a security audit on the current diff and flag any unencrypted secrets or missing authorization headers.
Taking it a step further, integrating Claude with GitHub Actions allows the AI to automatically comment on Pull Requests, providing summaries or suggesting fixes for linting errors before a human even looks at the code.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even with the best Claude coding prompts, it’s easy to fall into “amateur” traps.
- The Concision Trap: Many developers think shorter prompts are better. In reality, verbosity that provides guidance is your friend. It’s better to be “too detailed” than to leave Claude guessing.
- Conflicting Instructions: Stacking too many “meta-instructions” (e.g., “Be concise but explain everything in detail”) confuses the model. Pick a lane.
- The Security Risk: Never ask Claude to “fix security” without a specific focus. AI can sometimes suggest patterns that look clean but are vulnerable to command injection if not properly sanitized.
- Over-Reliance: Claude is a “very fast intern,” not a senior architect. Always verify the logic, especially in critical paths. If you need to scale these capabilities, look into how-to-extend-claude-with-custom-agent-skills.
Frequently Asked Questions about Claude Prompting
How do I get Claude to output pure JSON?
To ensure Claude only returns JSON (and no conversational filler), use two techniques:
- Explicitly state: “Return ONLY a JSON object. No preamble, no postamble.”
- Prefilling: In the API or chat, start Claude’s response for it by typing
{. Claude will naturally continue the JSON structure.
What is the “Plan Before You Code” discipline?
It is the practice of forcing Claude to output a textual plan or a PLAN.md file before it writes any code. This allows you to catch logic errors or architectural mismatches early. It separates the “thinking” from the “typing.”
Can Claude Code handle large legacy codebases?
Yes, especially when using the Claude Code CLI or VS Code extension. These tools use “indexing” and “search tools” (like GrepTool) to find relevant snippets across thousands of files without exceeding the context window. Using a CLAUDE.md file is essential here to give the AI a map of the “legacy jungle.”
Conclusion
The transition from guessing to prompting is a journey from frustration to flow. By using the best Claude coding prompts, we aren’t just getting code; we are building a partnership with an intelligence that can handle the boilerplate while we focus on the high-level strategy.
At Clayton Johnson SEO, we believe that AI-assisted workflows are the future of both marketing and engineering. Whether you’re looking for SEO content marketing services or trying to optimize your internal dev team, the principles of clarity and structure remain the same.
Stay ahead of the curve by joining the Claude Code Masterclass newsletter. If you missed out on my year of Claude Code updates, where I covered every new feature, tip, and trick, I’ve got you covered — check out the complete list of Claude Code tutorials there, and do not forget to follow me on Medium.
Stop guessing. Start prompting. Let’s build something great.