The Ultimate Guide to Running AI Models via API
Why the Replicate API is Changing How Developers Deploy AI Models
The Replicate API is a cloud platform that lets you run, fine-tune, and deploy machine learning models without managing infrastructure. It provides production-ready APIs for thousands of AI models—from image generation to large language models—trusted by over 1,000,000 developers from startups to Fortune 500 companies.
Here’s what you can do with the Replicate API:
- Run models with a single API call using any programming language
- Fine-tune models with your own data to create specialized versions
- Deploy custom models using Cog, an open-source packaging tool
- Scale automatically from zero to millions of users without infrastructure work
- Pay per second of GPU compute time, with automatic scale-down to zero
| Core Feature | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Predictions | Create, get, list, and cancel model inference jobs |
| Trainings | Fine-tune models with custom datasets |
| Deployments | Run private model instances with dedicated hardware |
| Files | Upload and manage input/output files via API |
| Webhooks | Get notifications when predictions complete |
Unlike traditional ML infrastructure, Replicate handles API servers, dependencies, model weights, CUDA drivers, GPU allocation, and batching automatically. You authenticate with a bearer token, specify a model version and input parameters, and get back predictions—whether that’s generated images, text completions, or video outputs.
The platform supports diverse hardware options from CPUs ($0.000100/sec) to 8x Nvidia A100 GPUs ($0.011200/sec). Popular models like Google’s nano-banana have processed over 81.8M runs, while the replicate/hello-world model has served 5,681,081 runs, demonstrating production-scale reliability.
I’m Clayton Johnson, and I’ve spent years building AI-assisted marketing workflows and technical SEO systems that rely on scalable API integrations. Throughout this guide, I’ll show you how to leverage the Replicate API to integrate powerful machine learning capabilities into your applications without the operational overhead.

Getting Started with the Replicate API
Getting your hands on world-class AI models used to require a PhD in machine learning and a massive credit line with a cloud provider. Today, we can bypass all that. To start using the replicate api, the first step is creating an account at Replicate.
Once you are logged in, navigate to your account settings to find your API tokens. Replicate uses HTTP Bearer authentication. This means every request you send must include an Authorization header formatted as Bearer .
For those of us building production-grade applications, security is paramount. We never hardcode these tokens. Instead, we recommend using python-dotenv to store your REPLICATE_API_TOKEN in a .env file. This keeps your credentials out of source control and follows the same rigorous standards we discuss in our guide on why every developer needs AI tools for programming.
Finding Models with the Replicate API Search
With thousands of models contributed by the community, finding the “right” one can feel like looking for a needle in a haystack. Fortunately, the replicate api offers a dedicated search endpoint (currently in beta).
When you query this endpoint, Replicate doesn’t just return a list of names; it provides rich metadata, including:
- Generated descriptions: AI-summarized explanations of what the model does.
- Relevance scores: How well the model matches your query.
- Collections: Groupings like “Text to Image” or “Audio Generation.”
You can explore the full Search documentation to learn how to filter by model owner or popularity. For example, searching for “nano banana” will yield the high-performing image generation models mentioned earlier, complete with their unique model identifiers (e.g., google/nano-banana).
Authentication and Security Best Practices
As your team grows, sharing a single user token becomes a security nightmare. We suggest moving toward Service Accounts. Unlike user tokens, service accounts are tied to your organization rather than a specific individual.
Key benefits of this approach include:
- RBAC Policies: You can assign specific “Read Only” or “Admin” roles to different tokens.
- Persistence: The token remains active even if a specific developer leaves the company.
- Revocation: You can instantly rotate or delete tokens if they are compromised without affecting your entire user account.
Always ensure your tokens are stored in secure environments like AWS Secrets Manager or GitHub Secrets. If you’re managing complex deployments, check out the Replicated API token management settings for granular control over your team’s access.
Managing Predictions and Model Versions
In the replicate api, a “prediction” is the core unit of work. When you send an input to a model, you are creating a prediction object.
The prediction lifecycle typically follows this path:
- Starting: The infrastructure is spinning up.
- Processing: The model is actively running your input.
- Succeeded: The job is done, and the output is ready.
- Failed: Something went wrong (check the logs!).
- Canceled: You manually stopped the job.
To create a prediction, you need two things: the model identifier and a specific version ID. Model versions are immutable. This means if you find a version of a model that works perfectly for your app, it will never change. This is critical for production stability—you don’t want your image generator suddenly changing its style because the author updated the weights.
If a job is taking too long or was sent by mistake, you can always cancel a prediction to save on compute costs. This is especially useful when running heavy models like nano-banana, which has seen over 81.8M runs and can consume significant resources if left unmanaged.
Advanced Integration: Files, Webhooks, and Streaming
Modern AI applications rarely deal with simple text strings alone. You’ll likely need to handle images, audio files, or long-running video generations.
- File Uploads: For files under 256kb, you can use Data URLs. For anything larger, we recommend uploading the file to a public URL (like an S3 bucket) and passing that URL to the API.
- Webhooks: Instead of constantly polling the API to see if a prediction is finished, you can provide a
webhookURL. Replicate will send a POST request to your server the moment the status changes. See the guide on using webhooks with Replicate for a deep dive. - Streaming: For LLMs, waiting for the entire paragraph to generate can feel slow. Replicate supports Server-Sent Events (SSE), allowing you to stream tokens to your frontend in real-time.
Managing these advanced flows is similar to how we extend Claude with custom agent skills, focusing on asynchronous communication and robust error management. When an API call fails, the official Python library handles retries with exponential backoff automatically, ensuring your app stays resilient.
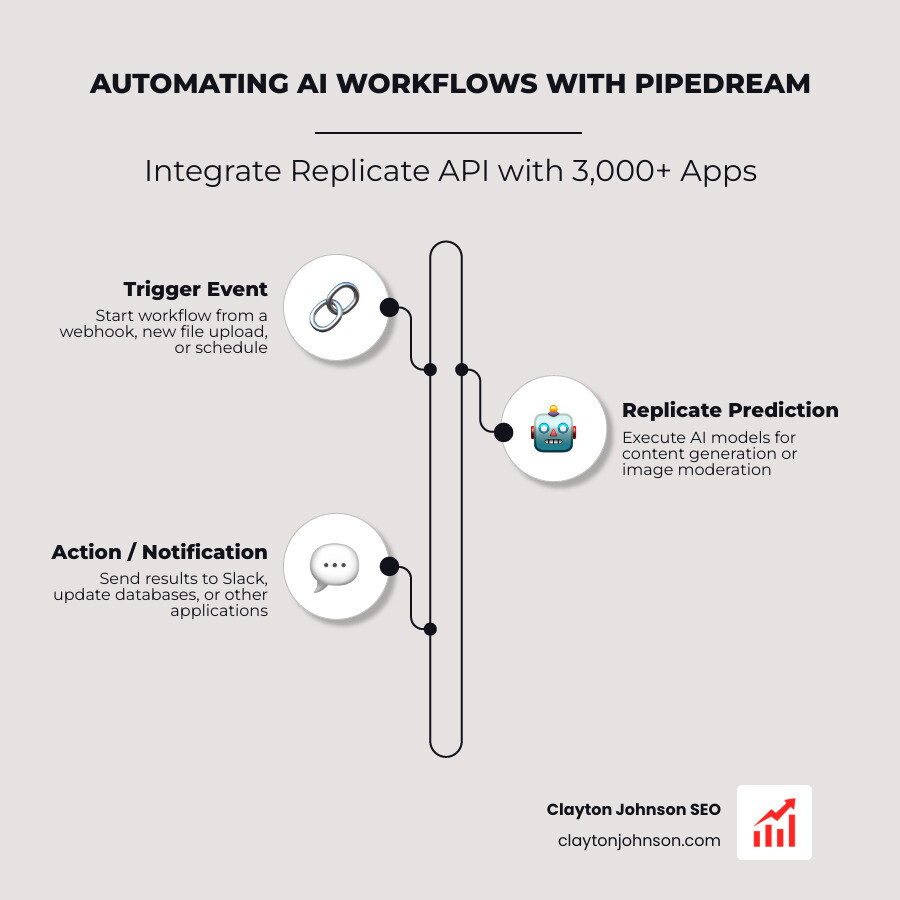
Building Workflows with Replicate API and Pipedream
If you want to build AI workflows without writing a mountain of “glue code,” Pipedream is our go-to recommendation. Pipedream connects the replicate api to over 3,000 other apps.
With the recent news that Pipedream has joined Workday, the platform’s enterprise capabilities are only growing. You can trigger a Replicate prediction whenever a new file is uploaded to Google Drive, or automatically moderate user-generated images by sending them through a content-safety model.
Whether you prefer Node.js or Python, Pipedream provides a serverless environment to orchestrate these tasks. This allows you to automate content generation or image moderation at scale without ever touching a server configuration.
Scaling, Pricing, and Custom Deployments
One of the most powerful features of Replicate is its “scale to zero” capability. If no one is using your app, you pay $0. When traffic spikes, Replicate spins up additional GPUs to handle the load.
We’ve broken down the hardware options to help you choose the right balance of speed and cost:
| Hardware Option | Price per Second | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | $0.000100 | Simple text processing, light logic |
| Nvidia T4 GPU | $0.000225 | Image restoration, small models |
| Nvidia A100 (80GB) | $0.001400 | Heavy LLMs, high-res video generation |
| 8x Nvidia A100 | $0.011200 | Massive parallel processing, training |
For those who need something more specific than what’s available in the community, you can deploy custom models using Cog. Cog is an open-source tool that packages your machine learning model into a standard Docker container. You define your environment in cog.yaml and your inference logic in predict.py.
This is the gold standard for the best AI for coding and debugging, as it allows you to bring your own proprietary code into a scalable cloud environment.
Frequently Asked Questions about Replicate
How do I handle rate limits and timeouts?
The replicate api is generous but not infinite. Most accounts can create 600 predictions per minute, while other endpoints (like listing models) allow up to 3000 requests per minute. If you hit these limits, you’ll receive a 429 Too Many Requests error.
To prevent your app from crashing, ensure your httpx timeout configuration is set correctly. We recommend a default timeout of 60 seconds for most requests, though long-running predictions should be handled via webhooks rather than holding an open connection.
What is the difference between official and community models?
Official models are maintained by the Replicate team or well-known research labs (like Stability AI or Meta). These models often have better documentation and guaranteed uptime. Community models are contributed by users. While many community models are production-ready, always check the model’s README and run statistics (like the 21.8M runs for z-image-turbo) to gauge reliability before integrating them into a mission-critical system.
How do I fine-tune a model like FLUX?
Fine-tuning allows you to teach a model a specific style or person. To do this, you create a “Training” job. You’ll need a dataset (usually a ZIP file of images) and a “trigger word.”
Refer to the FLUX fine-tuning guide for the exact parameters. Once the training is complete, Replicate creates a new model version under your username that only you (or your organization) can access. You can then run predictions against this custom version just like any other model.
Conclusion
The replicate api has effectively democratized AI development. By removing the infrastructure barrier, it allows us to focus on what actually matters: building great products and driving growth. Whether you are automating your content systems or building the next viral AI app, Replicate provides the stability and scalability you need.
At Clayton Johnson SEO, we specialize in building these types of AI-assisted workflows to help founders and marketing leaders dominate their niche. If you’re ready to integrate these tools into your own growth strategy, explore our SEO services or check out our frameworks for building high-performance content systems. Let’s make AI work for your business, not the other way around.