The Secret Sauce of Codegen and AI Tool Extensions

Why Codegen AI for Coding is Changing Software Development
Codegen ai for coding is changing how developers work by automating the low-level labor of software engineering—from planning features to writing tests to creating production-ready pull requests. Unlike traditional AI assistants that offer autocomplete suggestions, codegen agents autonomously understand requirements, generate code, iterate on mistakes, and deliver complete solutions.
Quick Answer: What is Codegen AI for Coding?
- Autonomous agents that plan, build, and review code with full context
- Production-ready output including PRs, tests, and documentation
- Deep integrations with GitHub, Slack, Linear, Jira, and your dev stack
- Enterprise-grade security with SOC 2 certification and isolated sandboxes
- Proven results: 230k+ pull requests created, 52% merge rate, $18.1M developer time saved
The paradigm shift is real. As one engineering leader observed, developers can now “select an entire backlog” and let AI agents complete tasks that used to require multiple team members. Non-technical users—even designers—are shipping production fixes without writing a single line of code.
But this isn’t about replacing developers. It’s about automating repetitive work so you can focus on higher-level strategy, architecture, and problem-solving. Codegen AI for coding handles the tedious mapping of problems to libraries, the boilerplate, the bug fixes, and the test suites.
The journey from autocomplete to agentic coding follows a clear progression: start with IDE extensions like Copilot, move to conversational tools like Claude or ChatGPT, adopt AI-enabled IDEs like Cursor, then lean into full agentic workflows with tools like Aider, GPT Pilot, or platforms like Codegen that orchestrate agents at scale.
The research shows that seniors use AI better than juniors because they know how to prompt effectively, evaluate outputs, and provide context. That’s where guidance matters. Junior developers can ramp up faster with AI—navigating unfamiliar codebases, exploring frameworks—but they need coaching on code review and prompt refinement to avoid the documented 9.4% bug increase from tools like Copilot.
Salesforce’s conversational AI programming paradigm demonstrates the future: natural language prompts generating executable code through iterative dialogue. The two-sum problem example in their CodeGen research shows how you can refine solutions from O(n²) to O(n) just by asking for a “hash map” approach. This isn’t sci-fi anymore—it’s production reality.
Enterprise adoption requires more than just cool demos. You need security (SOC 2 certification, pen tests), compliance (granular permissions, audit logs), integrations (Slack for notifications, Linear for ticket management), and observability (telemetry, snapshots, sandboxes). Platforms like Codegen provide the “OS for Code Agents” with these building blocks baked in, enabling deployment across thousands of teams.
I’m Clayton Johnson, and I’ve spent years building AI-assisted marketing workflows and growth systems that scale—experience that translates directly to understanding how codegen ai for coding fits into strategic operations. My focus is on creating durable systems where AI augments human expertise rather than replacing it, which is exactly how effective codegen adoption works.
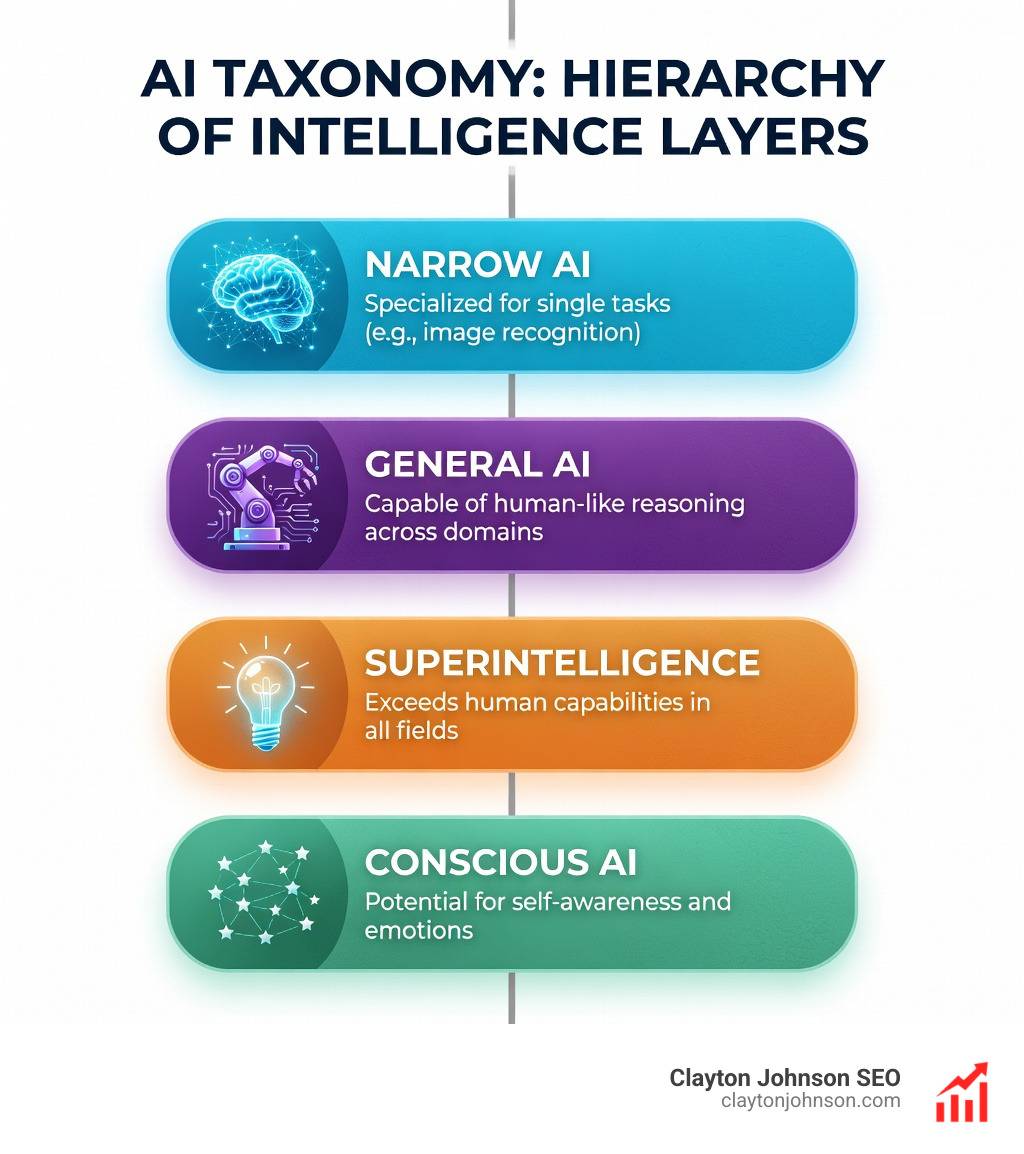
Basic codegen ai for coding vocab:
Understanding Codegen AI for Coding vs. Traditional Assistants
In the early days of AI-assisted development, we were impressed by simple autocomplete. You’d type a few characters, and the tool would guess the rest of the line. While helpful, it was essentially a “glorified spellcheck” for programmers. Today, codegen ai for coding has moved beyond these micro-suggestions into the field of full-scale agency.
The primary difference lies in autonomy and context. Traditional assistants like GitHub Copilot primarily function within the IDE as a reactive tool. You write code, and it suggests a completion. In contrast, modern code agents can take a high-level ticket from Jira, analyze the entire repository, plan a multi-file architectural change, execute the code in a sandbox, and submit a PR.

Platforms like Codegen helps you run frontier code agents at scale provide the necessary infrastructure—such as sandboxes and telemetry—to let these agents work safely. This transition is a major part of The real truth about coding AI growth, moving from “AI as a tool” to “AI as a coworker.”
The Evolution from Autocomplete to Autonomous Agents
The journey started with Intellisense and Zed autocomplete, which were limited by a small context window. Then came Codex, OpenAI’s series of models specifically trained on billions of lines of source code. According to the Code Generation Guide and Codex Docs, Codex models are the foundation for agentic software engineering, allowing developers to delegate entire tasks rather than just lines of code.
As we discuss in Mastering the Claude AI code generator for faster development, models like Claude 3.7 Sonnet have introduced “reasoning” capabilities. This allows an agent to think through a problem before writing a single line, reducing the “hallucination” rate that plagued earlier models.
Why Codegen AI for Coding is the New Standard
The new standard is defined by task orchestration. We are no longer just generating snippets; we are automating the “low-level labor” of engineering. This includes:
- Task Planning: Breaking down a feature request into actionable steps.
- Bug Fixing: Analyzing stack traces to identify and repair the root cause.
- Test Writing: Automatically generating unit and integration tests to ensure stability.
Understanding Why every developer needs AI tools for programming is crucial for staying competitive. For us, it means moving from being “coders” to being “orchestrators” who manage a fleet of digital agents.
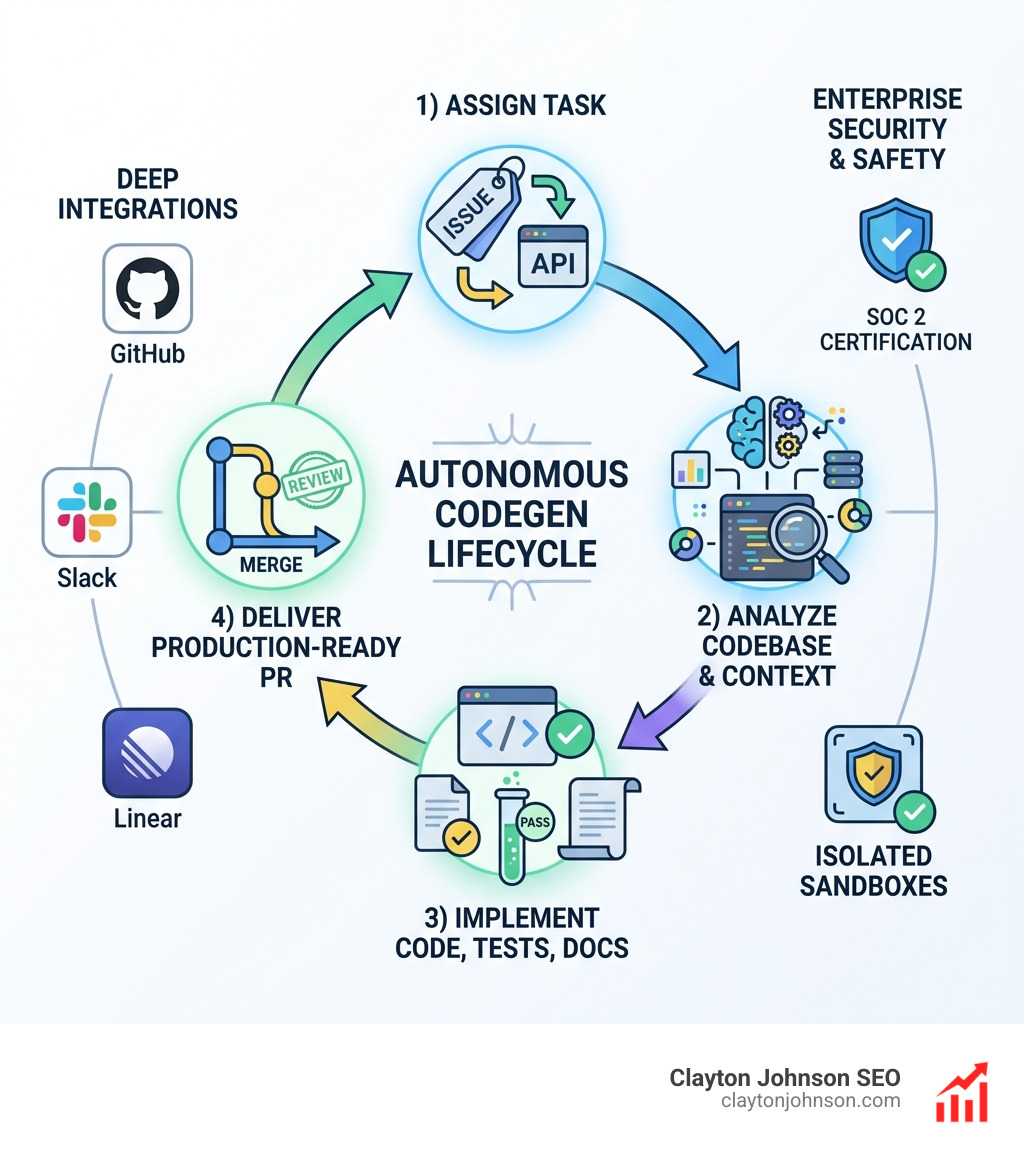
How Codegen Agents Work: From Prompt to Production-Ready PRs
The workflow of a modern code agent is typically categorized into four distinct phases: Assign, Analyze, Implement, and Deliver.
- Assign: A developer or manager tags the agent in a Slack channel, a Linear issue, or via an API call.
- Analyze: The agent scans the codebase to understand the existing architecture, dependencies, and patterns. It doesn’t just look at one file; it looks at the “full context.”
- Implement: Using models like GPT-4 or Claude, the agent writes the code, adds documentation, and creates tests. Tools like GPT Pilot take this further by iterating on mistakes—if the code fails, the agent “sees” the error and tries a different approach.
- Deliver: The agent creates a pull request (PR). In the case of Codegen, these agents have achieved a 52% merge rate, meaning more than half of their PRs are accepted with little to no modification.
This process is backed by the Research Paper on Conversational AI Programming from Salesforce, which highlights how large language models can solve complex problems like the “two-sum” algorithm through iterative dialogue.
The Hero’s Journey: Adopting Codegen AI for Coding Workflows
Adopting codegen ai for coding isn’t an overnight switch; it’s a “Hero’s Journey” for the developer.
- Step 1: Autocomplete: Getting used to Copilot’s suggestions.
- Step 2: Copy-Paste: Moving code to Claude or ChatGPT for debugging.
- Step 3: AI-Enabled IDEs: Switching to Cursor or Windsurf, where the AI has direct access to your files.
- Step 4: Agentic Coding: Using tools like Aider or Claude Code to run the agent directly in your terminal.
- Step 5: Full Delegation: Letting agents like those on the Codegen platform handle the “grunt work” while you play the role of the architect.
For those looking to master this, The complete Claude skill pack for modern developers offers a roadmap for moving from a manual coder to a “terminal jockey” who supervises robot-driven development.
Conversational AI Programming and the Non-Coder Revolution
One of the most exciting aspects of the codegen ai for coding movement is the democratization of software creation. The GitHub repository for CodeGen demonstrates how “Conversational AI Programming” allows users to describe an app in plain English.
For example, a designer can say, “Create a red button that calculates the mean Bitcoin price over the last 10 days,” and the AI “cooks” the program without the user needing to know Python or JAX. We’ve seen this first-hand: non-technical team members are now shipping production fixes. Learning How to extend Claude with custom agent skills is the next step for anyone wanting to build these custom capabilities into their own workflows.
Integrating Codegen AI for Coding into Your Enterprise Stack
For an AI agent to be truly useful in an enterprise setting, it can’t live in a vacuum. It needs to “work where you work.” This means deep integrations with the tools your team already uses.
- One-Click GitHub Install: Granting the agent access to your repositories via the One-Click GitHub Install is the first step.
- Slack Communication: You can Connect Slack for agent communication, allowing the agent to ask clarifying questions or provide progress reports directly in your team’s chat.
- Issue Management: By choosing to Connect Linear for issue management, the agent can automatically update ticket statuses, add comments, and link the PRs it creates.
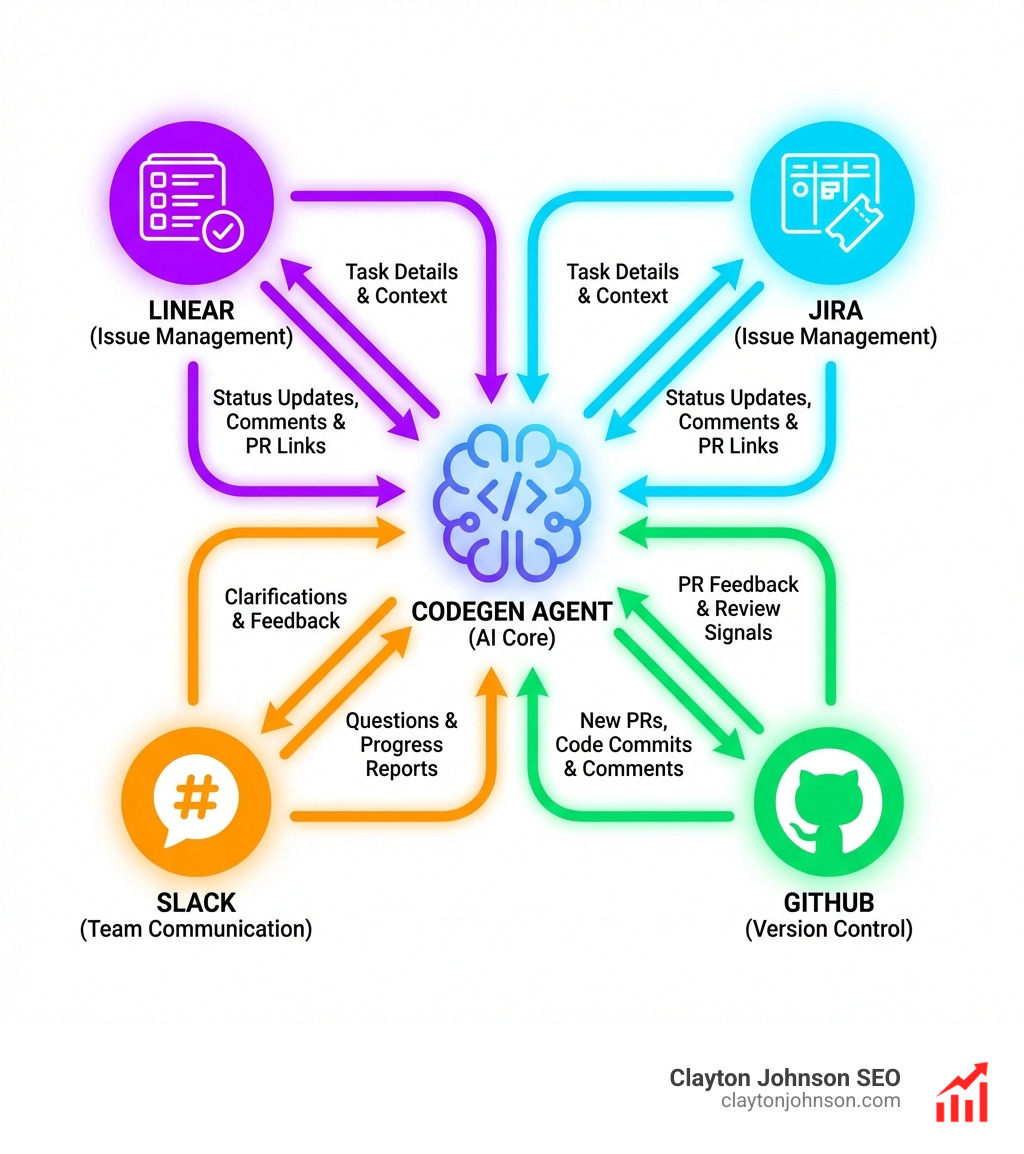
Automating the Low-Level Labor of Software Engineering
The goal is to eliminate the “toil.” We use codegen ai for coding to handle:
- PR Reviews: Agents can leave comments on human PRs, catching style issues or potential bugs.
- Auto-fixing Tests: If a CI/CD pipeline fails, an agent can analyze the log and commit a fix automatically.
- Documentation: Keeping READMEs and API docs up to date as the code changes.
The The best AI for coding and debugging isn’t just the one that writes the fastest code, but the one that integrates most seamlessly with your telemetry and sandboxes.
Scaling Frontier Code Agents Across Engineering Teams
We’ve seen the impact of scaling these agents across more than 1000 teams. The statistics are staggering:
- 230k+ Pull Requests created by autonomous agents.
- 52% Merge Rate, proving the code is production-quality.
- $18.1M in Developer Time Saved, allowing teams to ship features faster.
This is why Why your brand needs an AI growth strategy right now is so important. If your competitors are using agents to handle 50% of their coding tasks, you cannot afford to stay manual.
Security, Compliance, and Best Practices for AI-Generated Code
When you let an AI write code for your enterprise, security is the number one concern. Professional platforms must be SOC 2 Type I & II certified and undergo regular pen tests.
A core best practice is the use of isolated sandboxes. Every time an agent runs code or installs a dependency, it should happen in a secure, ephemeral environment. This prevents the agent from accidentally damaging your production systems or leaking data. The Codegen Security Overview details how these protections work to ensure that your code and data are handled with the highest standards.
Overcoming Limitations and the “Bug Rate” Challenge
We have to be honest: AI isn’t perfect. Research indicates that Copilot users introduced 9.4% more bugs than those not using the tool (as of December 2024). This happens when developers blindly accept AI suggestions without review.
To overcome this, we recommend:
- Human-in-the-loop: Always have a senior developer review agent-generated PRs.
- Formal Verification: Using memory-safe languages and hardcore test coverage.
- Trust Center: Regularly reviewing Trust Center for security documents and pen test results to ensure your provider is maintaining standards.
Best Practices for Prompting and Supervising Agents
To get the most out of codegen ai for coding, you need to be a “Prompt Engineer.”
- “Big Daddy” Rules: Establish core rulesets that the AI must never break (e.g., “Never use deprecated libraries”).
- Context Packing: Use tools like Repomix or repo2txt to slam your entire codebase into the LLM’s context window.
- Iterative Refinement: Don’t expect a perfect result on the first try. Use the GPT-5.1-Codex-Max prompting guide to learn how to guide the model through complex tasks.
Frequently Asked Questions about Codegen AI
How does Codegen AI differ from GitHub Copilot?
GitHub Copilot is primarily an autocomplete tool that suggests lines of code as you type. Codegen ai for coding refers to autonomous agents that can plan, implement, and deliver entire features or bug fixes by interacting with your ticketing systems and repositories.
Can non-coders really build apps using conversational AI?
Yes. Using paradigms like Salesforce’s CodeGen, users can describe their requirements in natural language. The AI then iterates with the user to “cook” the code, allowing designers or business analysts to ship production fixes and small apps without deep programming knowledge.
What are the security risks of using AI code agents?
The main risks include the introduction of bugs, security vulnerabilities, or the accidental exposure of sensitive data. These risks are mitigated by using SOC 2-certified platforms, running code in isolated sandboxes, and maintaining a strict “human-in-the-loop” review process.
Conclusion
The “Secret Sauce” of codegen ai for coding isn’t just the AI itself—it’s the integration of that AI into a robust, secure, and human-led workflow. By automating the low-level labor of software engineering, we empower our teams to focus on the high-level strategy that actually drives growth.
At Clayton Johnson SEO, we believe that AI-assisted workflows are the foundation of modern business strategy. Whether you are building software or scaling a content system, the principles remain the same: leverage the robot for the labor, and the human for the vision.
Ready to transform your development or marketing efficiency? Get started with SEO content marketing and see how we can help you build a durable, AI-powered growth engine today.