🧭 OVERVIEW:
A PESTEL Analysis is a macro-environmental scanning framework used to evaluate the external factors that can impact an organization’s strategy, performance, and market positioning. It examines:
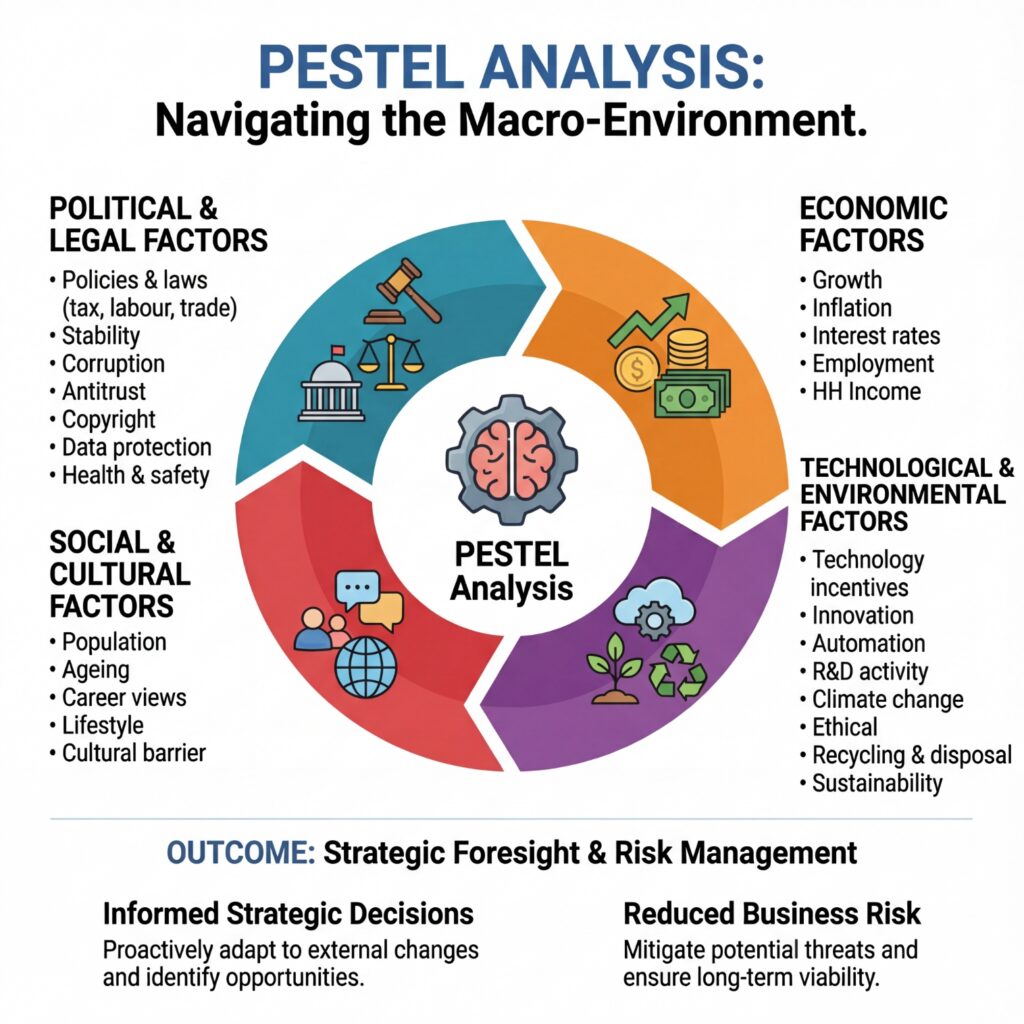
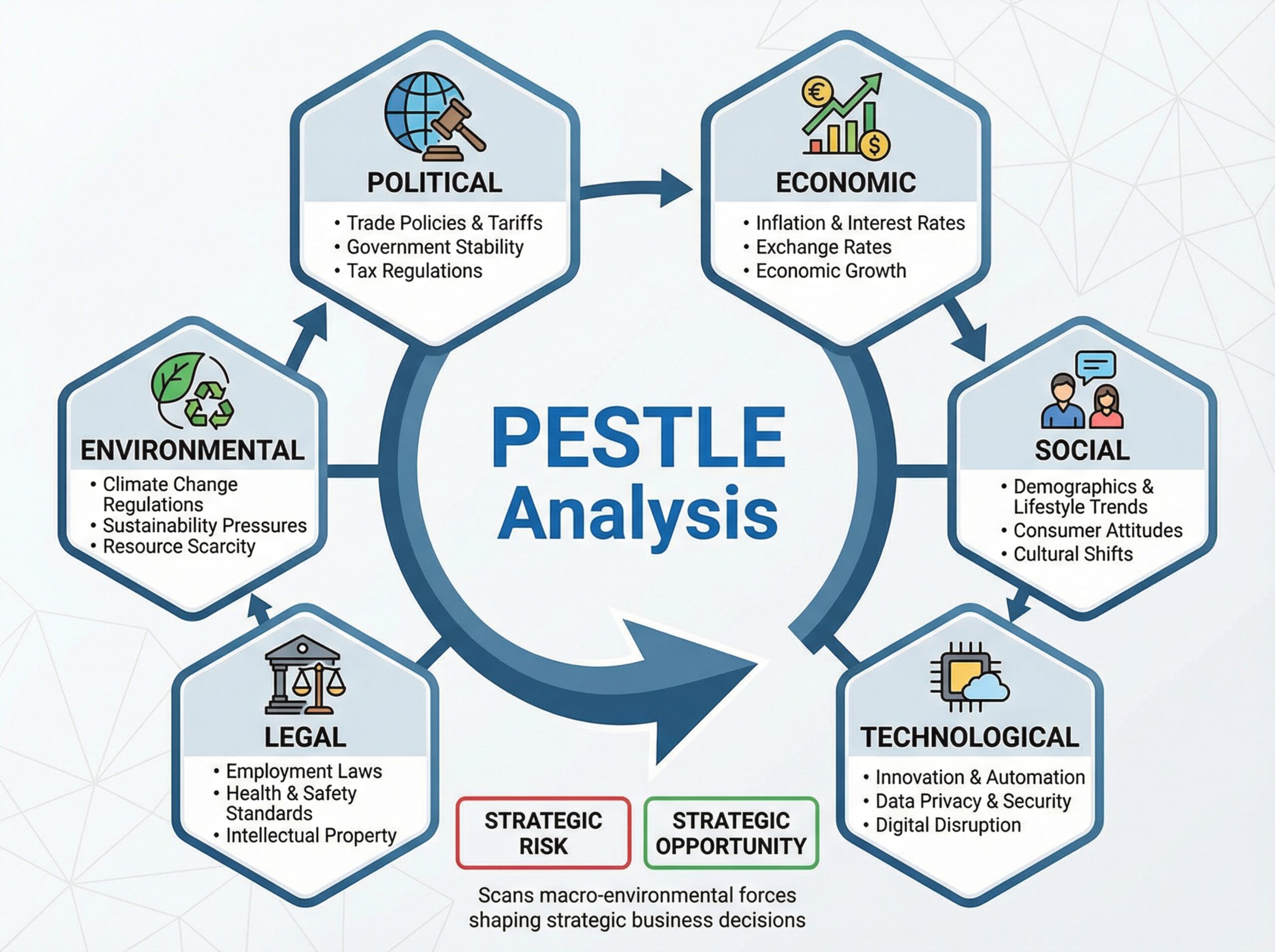
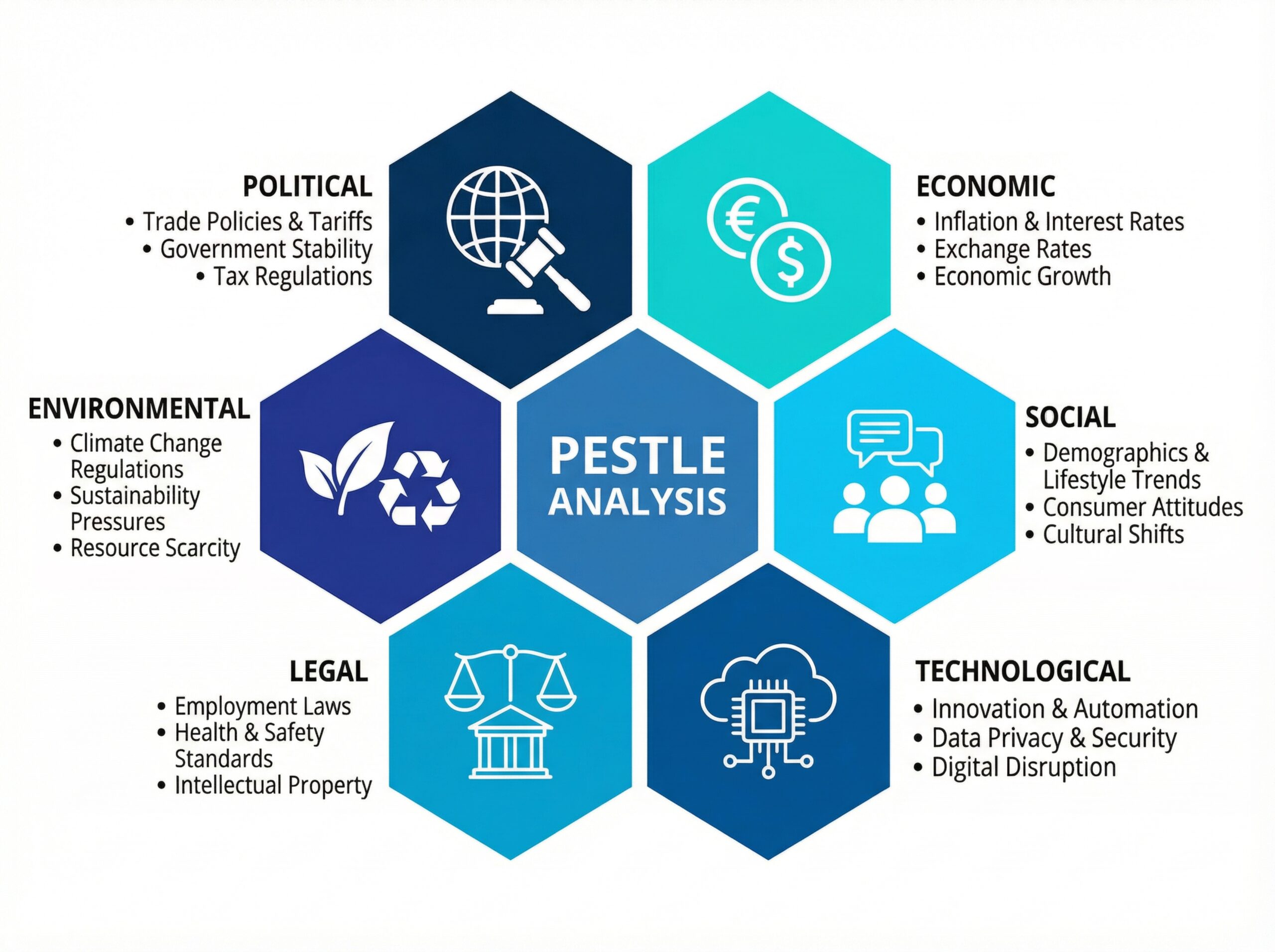
WHAT IS A PESTEL ANALYSIS?
Macro scan of Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental forces.
- Political
- Economic
- Social
- Technological
- Environmental
- Legal

Its purpose is to identify external opportunities and threats and feed them into a broader SWOT analysis, informing business strategy, market entry, product development, risk management, and long-term planning.
🧱 THE PESTEL FRAMEWORK
🏛 1. POLITICAL FACTORS
Definition: Governmental actions, leadership, and stability that influence the business environment.
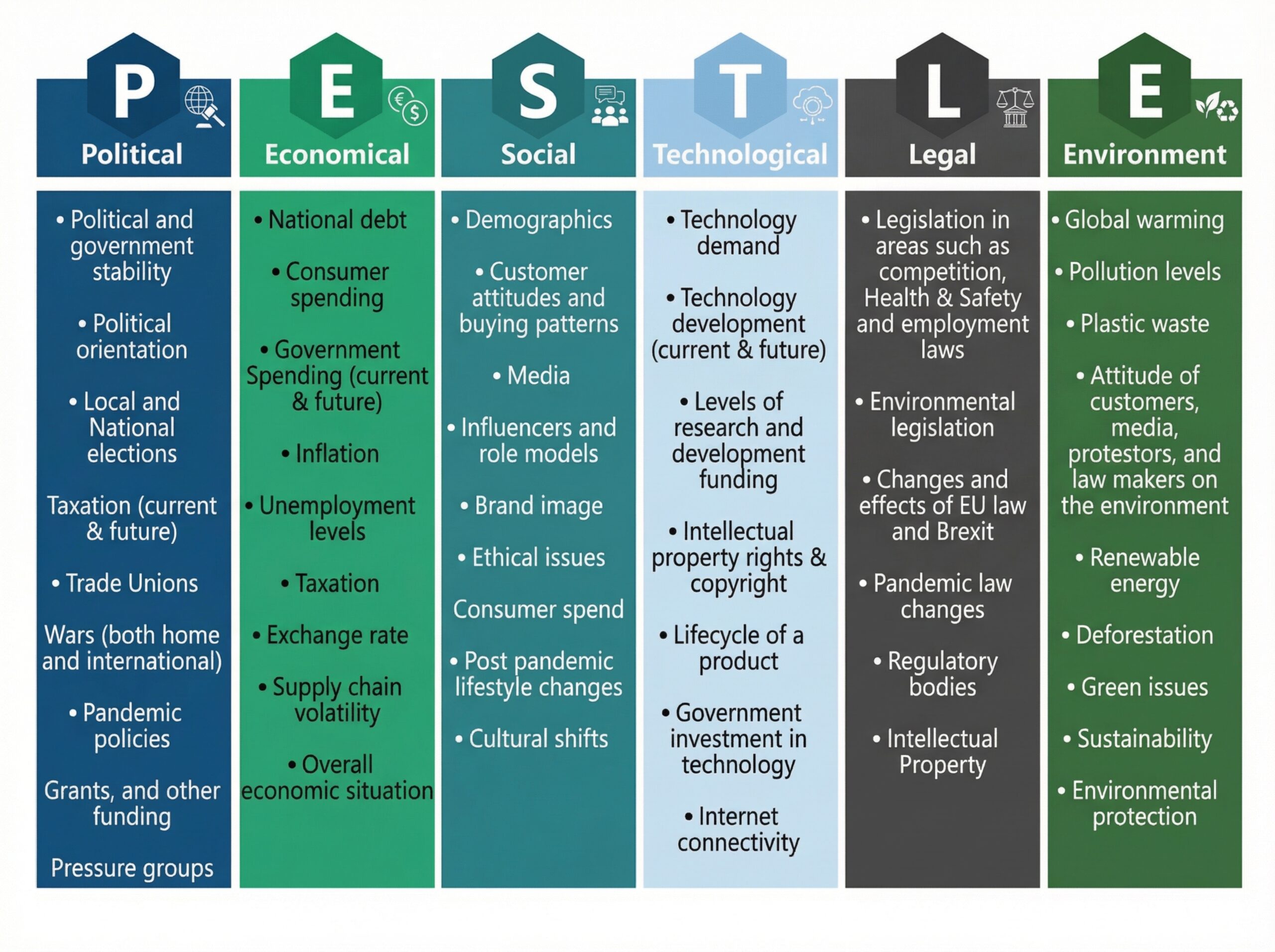
🔹 Examples of Political Factors:
- Government stability / regime changes
- Tax policies and fiscal legislation
- Trade regulations, tariffs, sanctions
- Corruption levels and lobbying
- Bureaucratic complexity
- National subsidies (e.g., for green tech)
📈 Real-World Impact:
- Market entry: Unstable political environments delay or block expansion
- Cost structure: Tariffs can raise prices on imported materials
🔍 How to Research:
- World Bank Governance Indicators
- CQ Researcher (deep dives on policies)
- Government websites (e.g., export.gov, trade.gov)
📌 Example: A government announces subsidies for EVs — an opportunity for battery manufacturers.
💵 2. ECONOMIC FACTORS
Definition: The state and dynamics of the economy influencing demand, cost, and investment.
🔹 Examples of Economic Factors:
- GDP growth, recession risk
- Inflation and interest rates
- Exchange rates
- Consumer and business confidence
- Employment levels and labor costs
- Disposable income shifts
📈 Real-World Impact:
- High interest rates: discourage borrowing, reduce expansion
- Unemployment: may reduce consumer demand but lower wage costs
🔍 How to Research:
- IBISWorld → Demand Determinants
- IMF, World Bank, data.census.gov
- Federal Reserve for interest/inflation trends
📌 Example: In high-inflation markets, companies pivot to essential goods.
👥 3. SOCIAL FACTORS
Definition: Demographics, cultural attitudes, lifestyle trends, and consumer expectations.
🔹 Examples of Social Factors:
- Aging or youthful populations
- Cultural attitudes (e.g., health, work-life balance)
- Education levels
- Urbanization and population density
- Generational buying behavior (e.g., Gen Z vs Boomers)
📈 Real-World Impact:
- Shapes marketing, product design, and recruitment
- Failure to understand cultural nuances can damage brand reputation
🔍 How to Research:
- Pew Research Center (attitudes, values)
- U.S. Census Bureau (demographics)
- Lifestyle surveys and social trend reports
📌 Example: Millennials value sustainability and ethical sourcing, impacting retail purchasing.
💻 4. TECHNOLOGICAL FACTORS
Definition: Innovations and emerging technologies that affect production, distribution, or communication.
🔹 Examples of Technological Factors:
- New production technologies (e.g., automation, AI)
- Digital transformation and R&D intensity
- Mobile and social media trends
- Cybersecurity advancements
- Patent trends and tech funding
📈 Real-World Impact:
- Drives disruption (as seen with Uber, Amazon, etc.)
- Delays in tech adoption can cause competitive disadvantages
🔍 How to Research:
- Gartner reports, TechCrunch, patent databases
- IBISWorld (Operating Conditions section)
📌 Example: Nokia and Blackberry missed the shift to smartphones — and lost market share.
🌱 5. ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
Definition: Ecological and sustainability issues, regulations, and climate considerations.
🔹 Examples of Environmental Factors:
- Carbon footprint and pollution regulations
- Resource scarcity and ethical sourcing
- Climate-related risks (e.g., hurricanes, wildfires)
- ESG criteria for investors
- Recycling and packaging laws (e.g., EU WEEE directive)
📈 Real-World Impact:
- Can impact supply chains, investor confidence, and regulatory costs
- Opportunity to create green competitive advantages
🔍 How to Research:
- CDP (Carbon Disclosure Project)
- Corporate sustainability reports
- ESG investment portals and government data
📌 Example: Companies meeting carbon goals may attract ESG investors.
⚖️ 6. LEGAL FACTORS
Definition: Laws and legal frameworks that directly impact operations and strategy.
🔹 Examples of Legal Factors:
- Employment law (e.g., wage mandates, safety standards)
- Consumer protection (e.g., product safety)
- Data privacy laws (GDPR, CCPA)
- IP/patent law
- Advertising regulations
- Industry-specific licensing
📈 Real-World Impact:
- Ignoring legal changes = fines or market bans
- Clear frameworks = opportunities for brand trust
🔍 How to Research:
- SEC filings (10-K → Risk Factors)
- Nexis Uni → court cases and legal news
- Regulatory body websites (e.g., FTC, OSHA, EU GDPR site)
📌 Example: Anticipating GDPR allowed companies to avoid major data breach fines.
📋 STEP-BY-STEP METHOD TO PERFORM A PESTEL ANALYSIS
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Brainstorm | List all external trends across the six PESTEL categories |
| 2. Identify Implications | How could each trend affect operations, costs, or strategy? |
| 3. Rate Importance | Label as Critical, Significant, or Moderate |
| 4. Assess Likelihood | Assign probabilities: Likely, Possible, Remote |
| 5. Consider Impact | Define what happens if it occurs and what action to take |
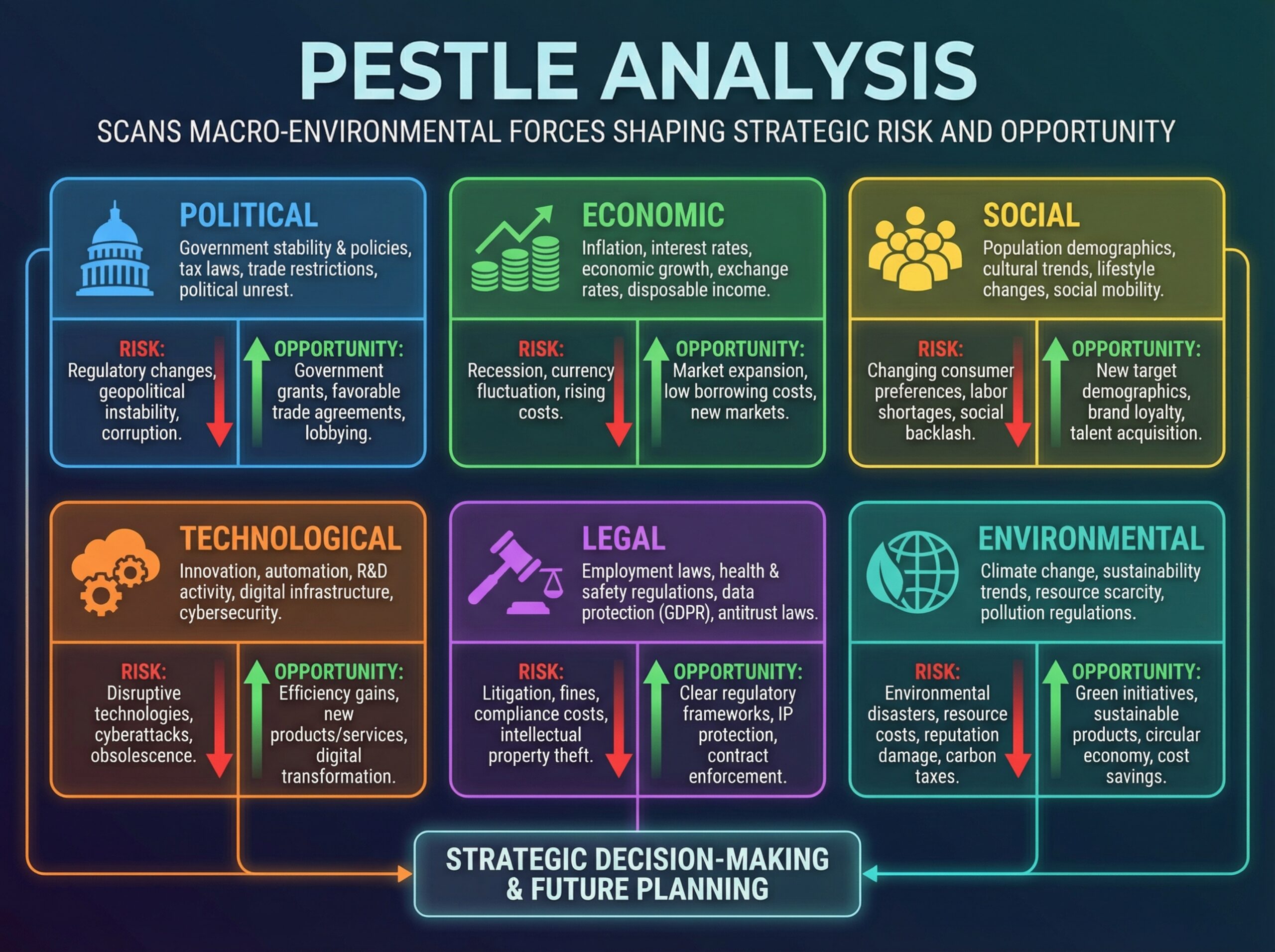
🔗 MAPPING PESTEL TO SWOT
| PESTEL Insight | SWOT Mapping | Strategic Response |
|---|---|---|
| Trade reform opens new markets | Opportunity | Expand internationally |
| Tougher data privacy laws | Threat | Invest in compliance systems |
| Tech adoption in the sector | Opportunity | Accelerate R&D initiatives |
| Environmental regulations | Threat | Rethink packaging and sourcing |
⚠️ LIMITATIONS & COMMON PITFALLS
| Risk | Description | Avoidance Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Analysis Paralysis | Getting stuck in data without decisions | Focus on key success factors |
| Bias | Cherry-picking trends that support your opinion | Use data triangulation |
| Irrelevance | Outdated trends or wrong geography | Set timeframes and scope |
| Over-reliance | PESTEL ≠ full strategy | Combine with SWOT + Porter’s Five |
🧠 FINAL INSIGHTS
🔹 PESTEL is a lens, not a conclusion. It sets the external stage for decision-making.
🔹 Use credible, triangulated sources for accuracy.
🔹 Always link insights back to business goals and strategic action.
🔹 Combine with SWOT, Porter’s 5 Forces, or market models for deeper impact.
✅ YOU ARE NOW READY TO:
- Conduct a full PESTEL Analysis
- Integrate insights into SWOT
- Prepare reports, market entry plans, and strategic reviews
- Guide teams with a structured external scanning process