Why Every Startup Needs a Risk Matrix Before Things Go Wrong
Risk matrix template download resources give startups a practical tool to identify, prioritize, and manage threats before they derail growth. Here’s what you need to know:
Quick Access Guide:
- 5×5 Risk Matrix – Most common format, scores risks 1-25 using likelihood × impact
- Excel Templates – Include conditional formatting, drop-down lists, and color-coded heat maps
- Key Components – Probability axis (rare to almost certain), impact axis (negligible to catastrophic), risk score calculation
- Free Sources – Available from project management platforms, WHS compliance sites, and industry organizations
- Calculation Methods – Multiplication method (1-25 range, emphasizes extremes) or addition method (2-10 range, linear scoring)
Most startups operate in survival mode. You’re moving fast, shipping product, chasing revenue. Risk assessment feels like something Fortune 500 companies do with consultants and three-ring binders.
But here’s the reality: the risks you don’t see are the ones that kill startups.
A vendor relationship implodes. A data breach compromises customer trust. A key technical dependency fails at the worst possible moment. These aren’t edge cases—they’re predictable patterns that destroy otherwise promising companies.
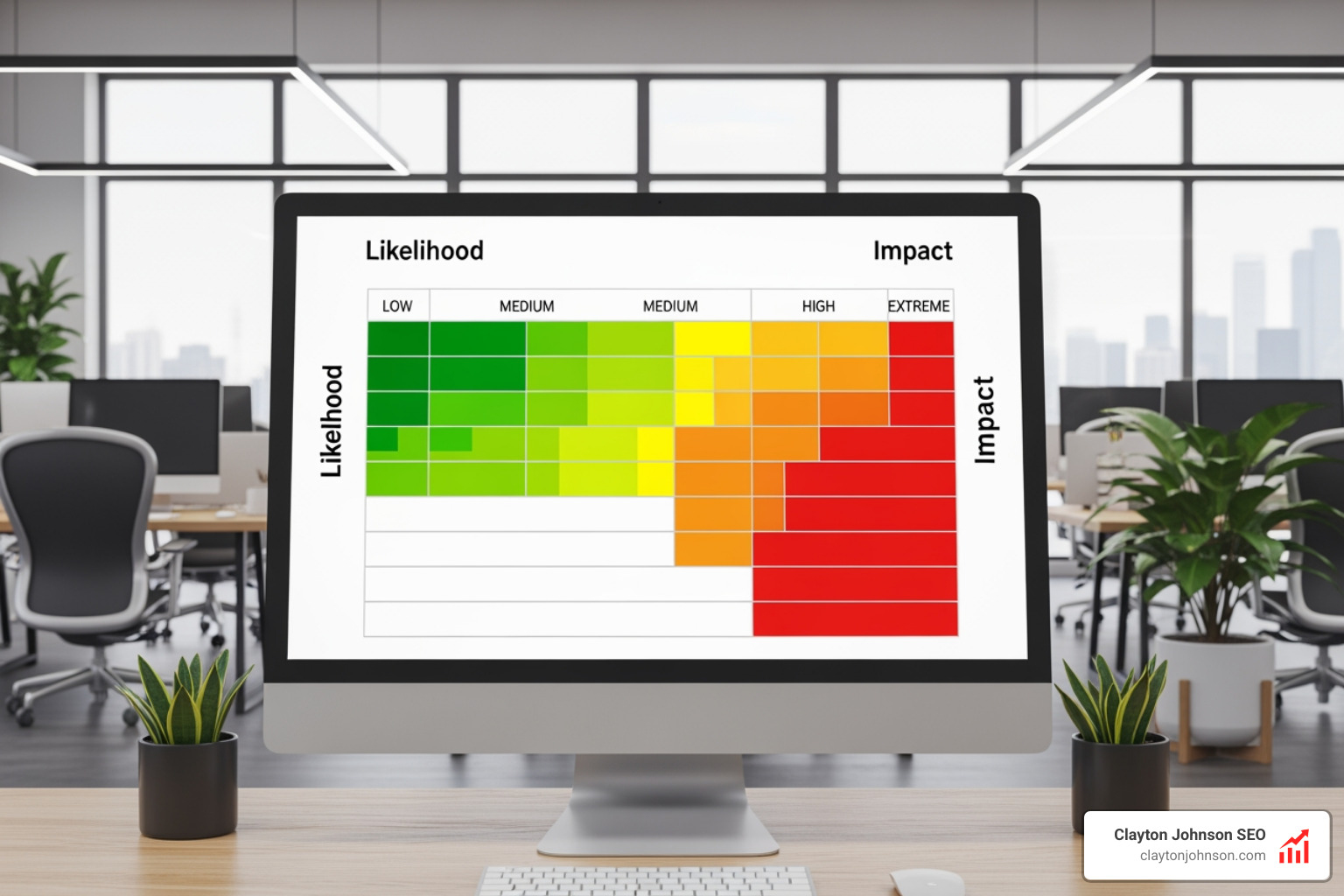
A risk matrix gives you a simple visual framework to plot threats by likelihood and severity. It’s not about preventing every possible failure. It’s about identifying which risks deserve immediate attention and which ones you can monitor. The color-coded grid—from green (low risk) to red (critical risk)—creates shared language across your team for discussing what matters.
The best part? You don’t need specialized training. With a well-designed template and clear rating definitions, you can run your first risk assessment in under an hour.
I’m Clayton Johnson, and I’ve helped founders build growth systems that account for strategic, operational, and technical risk across multiple scaling stages. Throughout this guide, I’ll show you how to download, customize, and actually use a risk matrix template download to spot vulnerabilities before they become emergencies—no consultant required.
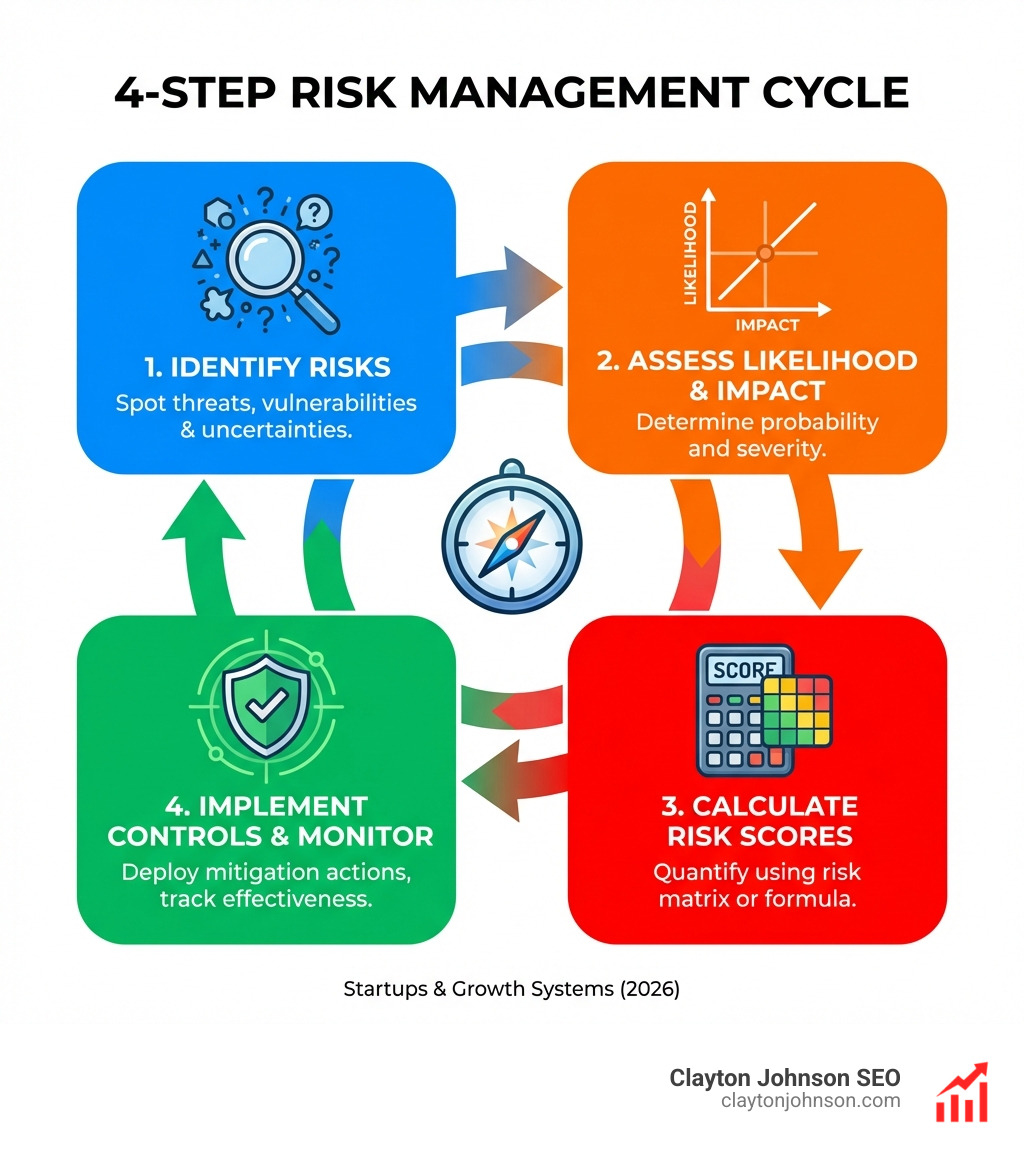
Understanding the Risk Matrix: A Startup’s Early Warning System
At its core, a risk matrix is a visual tool that allows us to see the “shape” of our problems before they hit us. Think of it as a weather radar for your business. It plots two specific variables against each other: Probability (how likely is this to happen?) and Impact (how much is this going to hurt?).

By using a “traffic light” system, we can instantly see which issues are in the “Red Zone” (stop everything and fix this) and which are in the “Green Zone” (keep an eye on it, but keep moving). This is a form of qualitative analysis that turns gut feelings into actionable data.
As noted by Harvard Business School Online, risk management isn’t just about avoiding bad things; it’s about making better decisions under uncertainty. For a startup, that might mean deciding whether to spend your last $10k on a new hire or a cybersecurity audit.
Defining Likelihood and Severity
To make a risk matrix template download work for us, we need to speak the same language. We define “Likelihood” (or probability) and “Severity” (or impact) using standardized scales.
- Likelihood Scales: These usually range from “Rare” (less than 1% chance) to “Almost Certain” (95%+ probability). In a technical setting, “Almost Certain” might mean a failure that happens once a week, while “Rare” might mean once a century.
- Impact Ratings: This measures the “pain level.” A “Negligible” impact might mean a one-day delay in a feature launch. A “Catastrophic” impact could mean the total loss of customer data or a legal event that shuts down the company.
According to Wikipedia’s overview of risk management, these scales help teams move away from vague terms like “it might happen” to specific, ranked categories.
Why Startups Need Structured Risk Assessment
Startups are uniquely vulnerable because they lack the “fat” or “buffer” that large corporations have. One bad operational slip-up can be terminal. We categorize these risks into four main buckets:
- Strategic Risk: Choosing the wrong market or a flawed business model.
- Financial Risk: Running out of runway or experiencing a sudden market shift.
- Operational Risk: Poor internal processes or vendor failures.
- Technical Risk: Security breaches, power outages, or “technical debt” coming due.
Using a structured approach ensures that we aren’t just reacting to the loudest problem, but the most dangerous one. This same structured thinking is what we apply to conversion optimization services, where we identify and mitigate the “risks” that prevent users from converting.
Choosing the Right Framework: 3×3 vs. 5×5 Risk Matrices
When you look for a risk matrix template download, you’ll usually find two main sizes: the 3×3 and the 5×5.
| Feature | 3×3 Matrix | 5×5 Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Low – Great for quick chats | Moderate – Standard for industry |
| Granularity | 9 levels of risk | 25 levels of risk |
| Best Use | Small projects / Daily standups | FMEA, WHS, and Strategic Planning |
| Sensitivity | Can miss nuanced differences | Highlights “Extreme” values effectively |
While a 3×3 is simple, we almost always recommend the 5×5 for startups. Why? Because it offers the granular depth needed for high-stakes decision-making. In a 5×5 matrix, “unacceptable risks” (usually scores 17-25) are clearly separated from “tolerable” ones, providing a much sharper trigger for action. Agencies like FEMA use these detailed models to manage natural disasters, where the difference between “High” and “Extreme” is a matter of life and death.
The Multiplication Method vs. Addition Method
How do you get that final number on your matrix? There are two common ways to calculate your risk score:
- Addition Method: (Likelihood + Impact). This creates a linear scale (usually 2-10). It’s simple but doesn’t always highlight how dangerous a high-impact, high-likelihood event truly is.
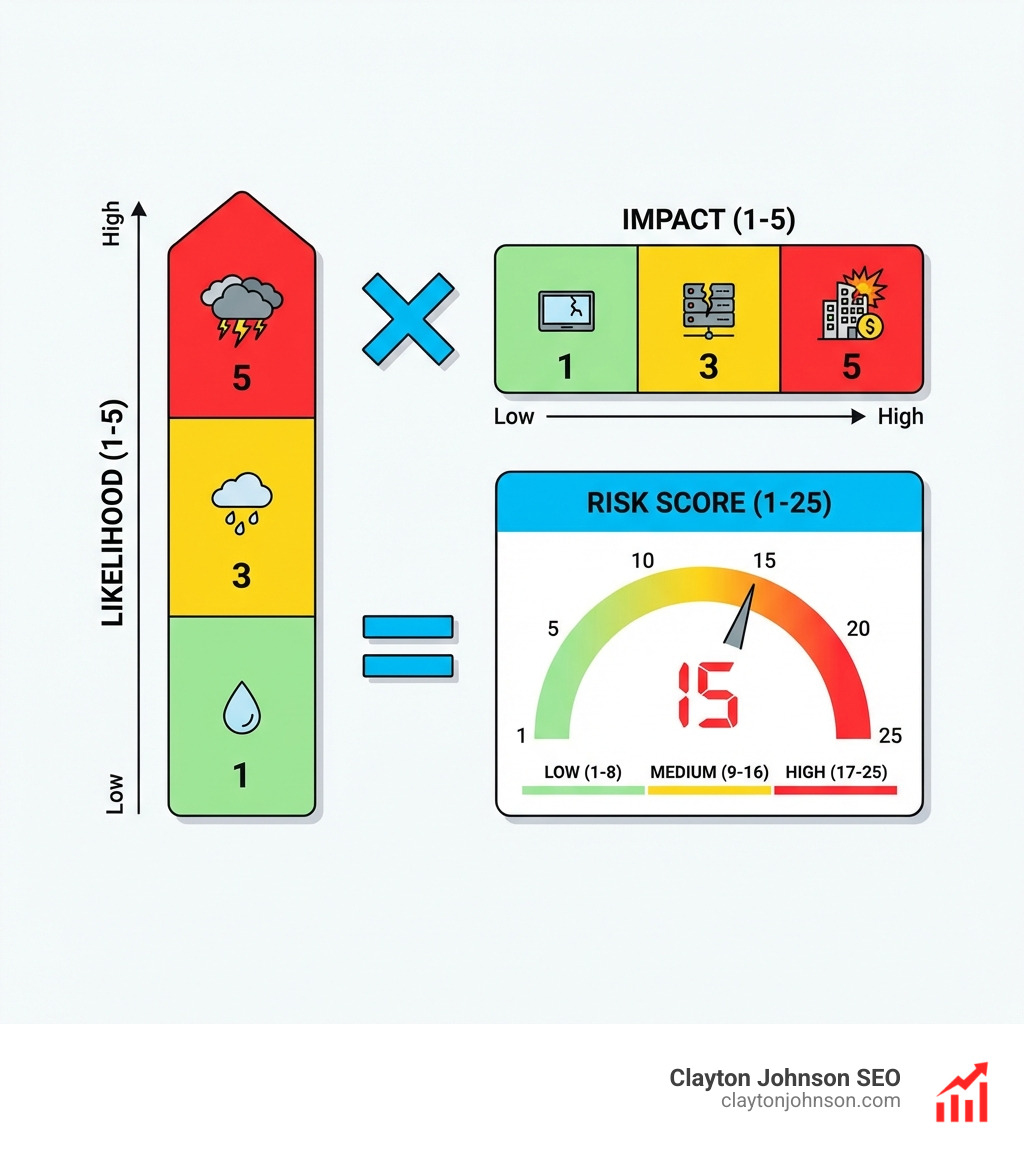
- Multiplication Method: (Likelihood x Impact). This is the industry standard, especially in Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). It results in a 1-25 range. Because it’s exponential, it pushes “Extreme” risks much higher than “Low” risks, making them impossible to ignore.
Advantages of the 5×5 Risk Matrix
The primary advantage of the 5×5 is its ability to handle “Extreme” values. In a startup, a risk that is “Rare” but “Catastrophic” (like a total database wipe) needs to be treated differently than something “Likely” but “Minor” (like a typo in a blog post). The 5×5 matrix makes this distinction obvious.
Step-by-Step: How to Use Your Risk Matrix Template Download
Once you’ve secured your risk matrix template download, it’s time to put it to work. Don’t just fill it out alone in your office—get the team involved.

- Identify Hazards: Brainstorm every possible thing that could go wrong. Be specific. Instead of “Technical Issues,” write “Primary AWS server outage.”
- Determine Initial Risk Score: Rate the likelihood and impact for each hazard before you do anything to fix it.
- Apply Control Measures: What can you do to lower the risk? (e.g., setting up a backup server).
- Score Residual Risk: This is the risk that remains after your controls are in place. If the residual risk is still too high, you need better controls.
Following a Code of Practice for risk management ensures that your process is systematic and defensible. We use a similar step-by-step architecture in our SEO content marketing services to ensure that every piece of content mitigates the “risk” of being invisible to search engines.
Where to Find a Reliable Risk Matrix Template Download
You don’t need to build this from scratch. Excellent free resources exist across various formats:
- Excel: Best for automated calculations and color-coding.
- Word/PDF: Best for printing and including in formal reports or WHS compliance folders.
- Specialized Templates: For example, cybersecurity-specific matrices focus on data breaches and malware.
Organizations like the HSE in the UK provide legal guidance on why these assessments are mandatory for protecting employees.
Setting Up Your Risk Matrix Template Download in Excel
If you’re using Excel, use Conditional Formatting to make the matrix come alive.
- Go to Home > Conditional Formatting > Color Scales.
- Set your “Midpoint” to 6. This ensures that your green-to-red transition happens at the right threshold for both addition and multiplication methods.
- Use Data Validation to create drop-down lists for Likelihood and Impact. This prevents team members from entering “High-ish” when they should be selecting a number from 1 to 5.
Industry-Specific Customization and Legal Standards
A tech startup in Minneapolis has different risks than a construction firm, but the underlying framework remains the same.

Customizing for IT and Cybersecurity
For IT startups, the focus shifts toward “Risk Speed” (how fast a threat can manifest) and “Organizational Vulnerability.” A data breach isn’t just a financial hit; it’s a reputational “Catastrophic” event. OSHA guidelines, while often associated with physical safety, increasingly recommend hazard assessments for all workplace environments.
Risk Assessment for Construction and WHS
In industries like construction, risk matrices are often a legal requirement. You’ll need to account for “Plant Risk” (heavy machinery) and site-specific hazards. Tools like Safe Work Method Statements (SWMS) integrate directly with your risk matrix. The CCOHS emphasizes that these assessments are the foundation of any robust health and safety program.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Risk Assessment
Even with a great risk matrix template download, things can go wrong if the process is flawed.
- Subjectivity Bias: One person’s “Likely” is another person’s “Possible.” Use quantitative definitions (e.g., “Likely = 50% chance within 6 months”) to align the team.
- Stagnant Data: A risk matrix is not a “one and done” document. It must evolve as your startup scales.
- Ignoring Residual Risk: Just because you have a backup doesn’t mean the risk is zero. Always calculate the “Residual Risk” to see if you’re truly safe.
Over-complicating the Rating Scales
Don’t get bogged down in decimal points. The goal is efficiency and alignment. If your team spends two hours arguing whether a risk is a 3.2 or a 3.4, you’ve lost the plot. Stick to whole numbers and clear qualitative definitions.
Failing to Assign Risk Ownership
A risk without an owner is a risk that will eventually happen. Every “Red” and “Orange” risk on your matrix must have a specific person—a Risk Owner—responsible for monitoring it and executing the mitigation plan.
Frequently Asked Questions about Risk Matrices
How do you calculate a risk score?
The most effective way is the Multiplication Method: Likelihood (1-5) x Impact (1-5). This gives you a score between 1 and 25. Scores of 1-6 are generally “Low,” 7-12 are “Medium,” 13-16 are “High,” and 17-25 are “Critical/Unacceptable.”
Who is responsible for maintaining the risk matrix?
While the Project Manager or Safety Officer often does the heavy lifting, the Business Executives (Founders) are ultimately responsible for approving the risk thresholds and ensuring resources are allocated to mitigation.
How often should a risk matrix be updated?
At a minimum, we recommend an annual review. However, for fast-moving startups, you should update it at the start of every new project, after any significant incident (a “post-mortem”), or when there’s a major shift in the market or workplace.
Conclusion
Building a startup is inherently risky, but you don’t have to fly blind. By using a risk matrix template download, you’re installing a “growth architecture” that protects your hard work.
At Demandflow.ai, we believe that Clarity → Structure → Leverage → Compounding Growth. A risk matrix provides that clarity and structure, allowing you to focus your energy on growth rather than constant firefighting.
If you’re ready to stop guessing and start building a structured growth engine for your business, I’d love to help.
Work with me to turn your startup’s chaos into a scalable, risk-aware system.