How to use AI audits to spot the invisible
Why how to use AI audits matters for strategic risk management
How to use AI audits effectively requires a structured framework that goes beyond surface-level compliance checks. At its core, an AI audit evaluates whether your AI systems follow secure, legal, and ethical standards—examining data outputs, model architectures, and real-world impacts across your organization’s entire AI footprint.
The quick answer: To use AI audits effectively, you need to:
- Form a cross-functional audit team from legal, compliance, IT, and HR
- Map all AI tools and providers across your organization
- Identify applicable regulations and categorize systems by risk level
- Assess bias through technical reviews and stakeholder interviews
- Review vendor contracts for liability and security provisions
- Document everything transparently throughout the AI lifecycle
- Implement continuous monitoring with defined KPIs and alerts
The stakes are higher than most organizations realize. AI-powered tools can perform audit fieldwork up to 50x faster than traditional methods, but speed without structure creates more noise than insight. Without a clear audit framework, teams generate scores, charts, and recommendations that never translate into meaningful action. Meanwhile, AI systems increasingly shape how your brand appears in search results, how hiring decisions get made, and how operational risks compound invisibly.
The challenge isn’t just technical—it’s architectural. Modern AI audits must address algorithmic transparency, detect hidden bias in training data, ensure GDPR compliance, and evaluate third-party vendor solutions simultaneously. Organizations face a regulatory patchwork spanning NYC’s Local Law 144 for employment tools, the EU AI Act’s risk-based framework, and evolving state-level requirements across Illinois, Texas, and Connecticut. The complexity multiplies when AI systems evolve continuously, making one-time audits obsolete before implementation finishes.
I’m Clayton Johnson, an SEO and growth strategist who helps organizations build structured systems for AI visibility, content infrastructure, and strategic diagnostics. I’ve spent years helping marketing and operations leaders understand how to use AI audits not just for compliance, but as a competitive advantage—transforming fragmented AI adoption into measurable strategic leverage.
Similar topics to how to use ai audits:
What is an AI Audit and Why is it Essential?
An AI audit is a formal evaluation of an artificial intelligence system to ensure it operates within secure, legal, and ethical boundaries. It isn’t just a technical “bug check”; it is an investigation into algorithmic integrity. We look at the data going in, the logic processing that data, and the real-world consequences coming out.
Why do we need this now? Because AI is no longer a “nice-to-have” experiment; it is the engine running our businesses. Statistics show that nearly half of enterprise tech leaders now make AI a core component of their business strategy. However, only 6% are “AI high performers” who actually see a significant EBIT impact. The difference between the two often comes down to governance.
Without a structured audit, organizations face massive compliance gaps. In Minnesota, for example, the Meaningful Standards for Auditing High-Stakes AI emphasize that high-stakes systems—like those used in hiring or finance—require rigorous external evaluation to prevent harm.
Beyond legalities, there is the issue of brand reputation. If your AI starts hallucinating or showing bias, the fallout is public and painful. By Growth Auditing in the Age of AI, we ensure that our tools aren’t just fast, but they are also reliable and aligned with our ethical standards.
How to use AI audits to identify and mitigate bias
One of the most critical reasons to learn how to use AI audits is to catch algorithmic bias before it causes real-world harm. Bias in AI isn’t usually intentional; it’s an “invisible” reflection of historical prejudices found in training data or flawed assumptions made during development.
Identifying the “Moments of Bias”
Bias can enter the lifecycle at several stages:
- World to Data: When historical inequalities are baked into the datasets used for training.
- Predictions to Decisions: When a technically “accurate” model leads to unfair real-world outcomes.
To audit for this, we use fairness metrics like demographic parity (ensuring the system treats different groups equally) and equal opportunity. According to the Stanford HAI Policy Brief on Algorithm Audits, audits must be continuous because a “fair” model today can drift into bias tomorrow as new data is introduced.
Mitigation Strategies
- Protected Groups: Clearly define which groups (based on race, gender, age, etc.) are at risk of discrimination.
- Human Oversight: Never leave the final decision to the machine. Implement “human-in-the-loop” systems to review AI outputs.
- De-biasing Techniques: If an audit uncovers bias, we may need to retrain the model with more representative data or adjust the algorithm’s weights.
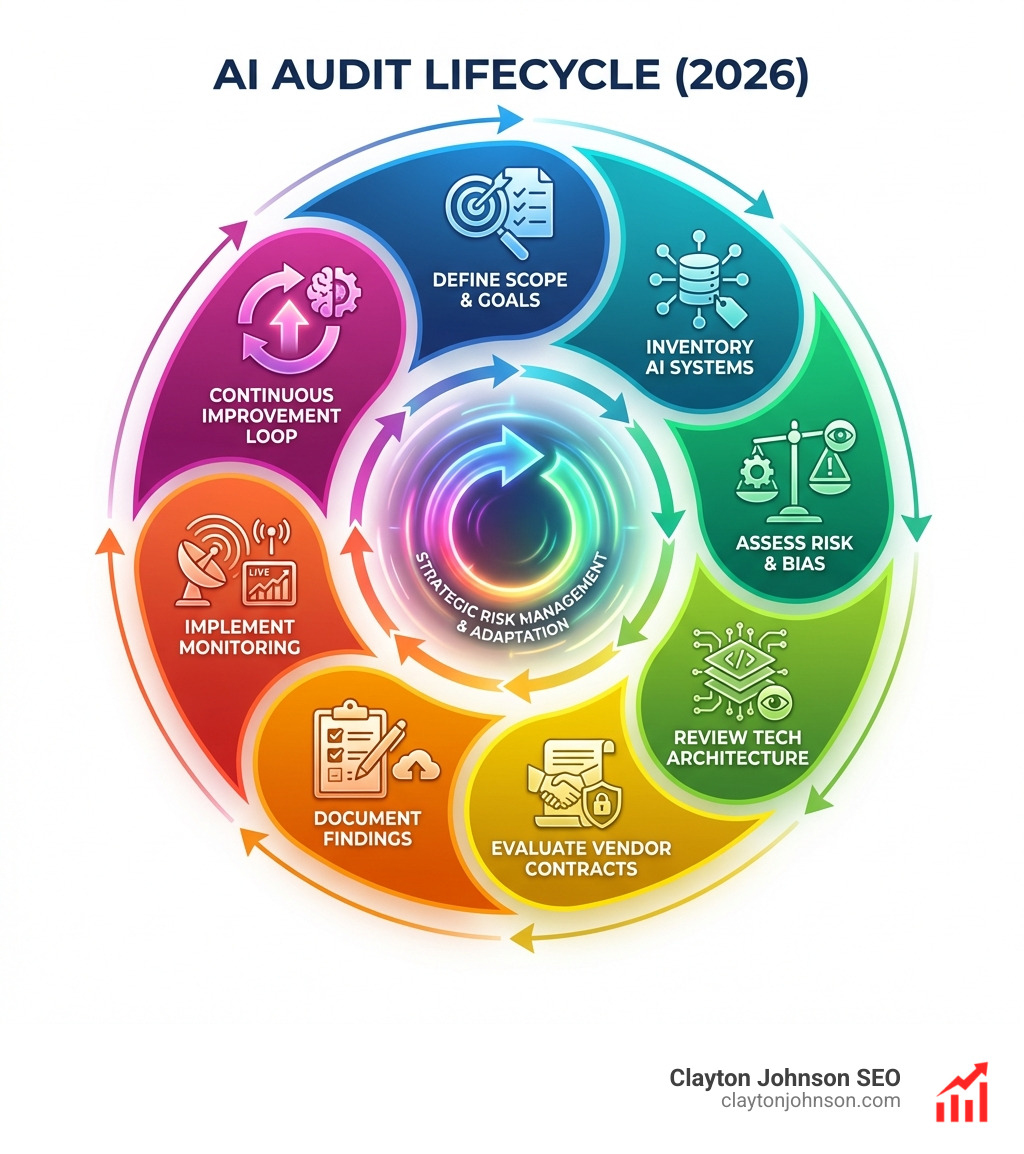
Fundamental steps for conducting a comprehensive AI audit
Conducting a comprehensive audit requires a move away from siloed departments. You can’t leave this just to the IT team.
- Form a Cross-Functional Team: Bring together experts from Legal (for compliance), HR (for ethical use), IT (for technical architecture), and Compliance.
- AI Mapping: Create a living inventory of every AI tool in use. This mirrors the data mapping process used in privacy programs.
- Risk Categorization: Not every tool needs a deep dive. A tool that summarizes internal meetings is low-risk; a tool that screens resumes is high-risk. Categorize them as High, Medium, or Low based on their impact on human lives and data sensitivity.
- Technical Review: Analyze the AI-Driven SEO Audits and data pipelines. Where does the data come from? Is it clean? How is the model hosted?
How to use AI audits for data privacy and security
Data is the fuel for AI, which makes it a massive target for security breaches. During an audit, we must verify that the organization is adhering to data minimization—only collecting what is strictly necessary.
We check for:
- GDPR Compliance: Ensuring users have the “right to explanation” for automated decisions.
- Anonymization: Using The Top Automated SEO Audit Tools to verify that PII (Personally Identifiable Information) is redacted before it hits the model.
- Encryption Protocols: Verifying that data is protected both at rest and in transit.
How to use AI audits to evaluate vendor solutions
Most companies don’t build their own AI; they buy it. This means your risk is often in someone else’s hands. An AI audit must include a deep dive into third-party contracts.
Use an How to Audit AI Checklist to look for:
- Liability and Indemnification: Who pays if the AI makes a mistake?
- Service SLAs: What are the uptime and accuracy guarantees?
- Data Residency: Where is your data actually being stored? (Crucial for international regulations).
- SOC 2 Type II Reports: Does the vendor have independent verification of their security controls?
Leveraging AI tools to enhance internal audit efficiency
Ironically, the best way to audit AI is often by using AI. Traditional auditing relies on statistical sampling—checking maybe 5% of files and hoping for the best. With AI, we can achieve 100% population analysis.
| Feature | Manual Audit | AI-Driven Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Weeks or Months | Minutes or Hours |
| Scope | Statistical Sampling (1-5%) | 100% Population Analysis |
| Accuracy | Prone to human fatigue/error | Highly consistent; flags anomalies |
| Focus | Checking boxes | Identifying high-risk patterns |
When Content Auditing for Humans Who Use Robots, we use AI to perform trace grading. This involves assigning scores to an AI agent’s end-to-end log of decisions. Instead of a “black-box” where we just see the result, we can see the “reasoning” steps the AI took. This allows us to spot “hallucinations” or logical errors at scale.

Overcoming challenges in AI audit implementation
It isn’t all smooth sailing. Organizations face significant hurdles when trying to implement these systems.
- Skill Gaps: There is a severe shortage of workers who understand both traditional audit processes and complex machine learning.
- Black-Box Opacity: Some advanced neural networks are so complex that even their creators struggle to explain why a specific output was generated. This makes “explainability” a primary goal of the audit.
- Hallucination Risks: AI can confidently present false information. Auditors must use “graders” to validate AI responses against known facts.
- Regulatory Patchwork: Without a single federal AI law in the US, companies must navigate a messy mix of state and local rules.
To overcome these, we recommend starting small. Don’t try to audit every system at once. Pick one high-impact area—like your SEO content architecture—and build a defensible audit workflow there first.
Frequently Asked Questions about AI Audits
How often should organizations conduct AI audits?
We recommend comprehensive AI audits at least annually, but high-risk systems (like those handling financial data or hiring) should be reviewed quarterly. You should also trigger an audit whenever a new tool is deployed, a major regulation changes, or the model undergoes significant retraining.
What are the best practices for continuous monitoring?
Post-audit, you need a “living” dashboard. Establish KPIs for:
- Accuracy Rates: Is the model’s performance degrading over time?
- Bias Metrics: Are certain demographic groups seeing different outcomes?
- Compliance Incidents: Track any near-misses or data privacy flags.
- Automated Alerts: Set up triggers that notify the audit team if the model’s output deviates from established guardrails.
What legal frameworks apply to AI auditing?
Currently, the landscape is a “patchwork.” Key frameworks include:
- EU AI Act: The gold standard for risk-based AI regulation.
- NYC Local Law 144: Specifically requires bias audits for automated employment tools.
- GDPR: Governs how personal data is used in automated decision-making.
- NIST AI RMF: A voluntary but highly respected framework for managing AI risk.
Conclusion
Learning how to use AI audits is about more than just staying out of legal trouble; it’s about building a structured growth infrastructure. When AI-generated content and automated decisions are becoming the norm, the companies that win will be the ones that can prove their systems are transparent, fair, and reliable.
At Clayton Johnson SEO, we believe that clarity leads to structure, and structure leads to leverage. By implementing a rigorous AI audit lifecycle, you aren’t just mitigating risk—you are future-proofing your brand for the age of AI Search Strategy.
Don’t let your AI operate in the dark. Use these audits to spot the invisible, fix the structural gaps, and build a foundation for compounding growth. Reach out to us to learn how we can help you architect a safer, faster, and more effective AI ecosystem.